US Neurology Devices Market Analysis
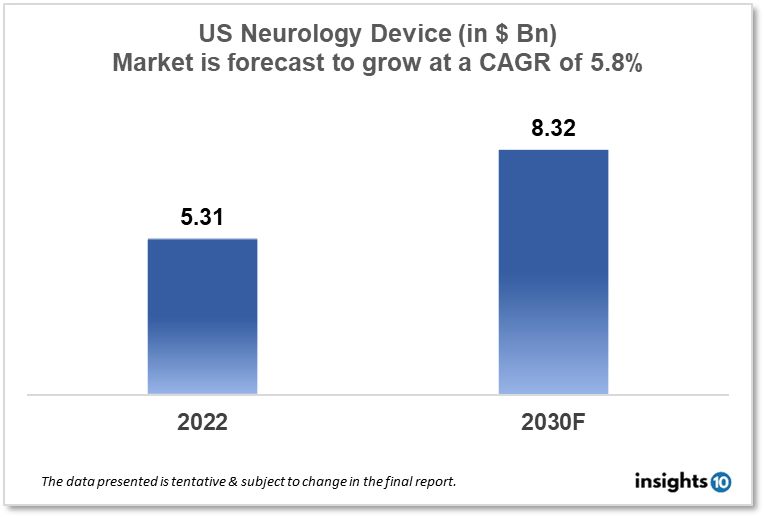
The US Neurology Device Market size is at around $5.31 Bn in 2022 and is projected to reach $8.32 Bn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period. With increasing emphasis on minimally invasive procedures and revolutionary research being focussed on Neurology diseases like ALS, Alzheimer’s disease, and traumatic Neurology impairment. Major players like Medtronic, GE Healthcare, and Siemens Healthineers are capturing a wider network of stakeholders. This report by Insights10 is segmented by product type like neurostimulation, interventional neurology, neurosurgery devices, and neuro-endoscopes, and by the end user.
Buy Now

US Neurology Device Market Executive Summary
Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, major depression, epilepsy, spinal cord injury, and traumatic brain injury are just a few of the Neurology disorders and conditions that Neurology devices can assist diagnose, preventing, and treating. Neurology gadgets can assist restore hearing and sight and boost function in those who have limb loss or congenital limb abnormalities. Neurodiagnostics, neuro-interventional, and neurostimulation devices are examples of Neurology devices. The FDA's Centre for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) Neurology Program performs regulatory science research to assist ensure patient access to innovative, safe, and effective neurology devices. The Neurology device market is expanding rapidly, notably in the areas of device interfaces, and interventional and surgical Neurology devices. Despite tremendous technical development, collecting samples from the nervous system remains difficult, and systemic markers are frequently unavailable. Neurology gadgets have substantial challenges in clinical testing for safety and effectiveness. Developing regulatory tools, methods, and models to aid in the understanding of clinical manifestations of Neurology diseases, as well as non-clinical methods to assess the safety of these devices, presents an opportunity to significantly reduce the regulatory burden associated with bringing potentially life-saving devices to market. The FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) conducts research to promote science-based and transparent judgments in the device review process while minimizing assumptions and subjectivity. FDA scientists promote regulatory science by creating new tools, standards, and methodologies for evaluating the safety, effectiveness, quality, and performance of pharmaceuticals and medical devices.
The development of more dependable brain interface devices is one area of FDA regulatory science for Neurology devices. The US Neurology Device Market size is at around $5.31 Bn in 2022 and is projected to reach $8.32 Bn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period (2022-2030). Finding new systems-level biomarkers for Neurology illnesses, contrasting invasive and non-invasive neural interface technologies to assess their durability and efficacy, and new techniques for data analysis and display to get the most valuable data out of physiological recordings. creating test procedures to measure cognitive strain and upper limb prosthetic performance, changes brought on by cortical implants in terms of neurophysiology, anatomy, behavior, and the characteristics of electrode materials. Metrics for measuring how well peripheral nerve contacts perform over the long run. identification of brain damage Applications of high-intensity therapeutic ultrasound to the diagnosis and treatment of brain injuries, as well as the long-term reliability of neural implants under the guidance of a cranial robotic platform, precisely match your surgical goals for cranial procedures. You may rapidly and precisely align your surgical plans for cranial procedures thanks to continuous real-time visualization, feedback, and robotically aided movement.
The innovative research in the direction of surgical guidance in neurology strives to improve workflow efficiency with a minimal footprint that is it seamlessly integrates with your navigation system with optical and electromagnetic trackers with the drilling technology. This guides the bone anchor along a predetermined path and the target area is reached by passing a flexible laser catheter through the bone anchor. Installation of the anchor bolts to allow for the installation of depth electrodes helps efficiently place multiple electrodes. In the newer devices, high-speed pneumatic drills with a permanently attached tracker allow for intraoperative navigation of spinal procedures using the surgical navigation system which is a precision device for spinal cord surgeries and has been popular with surgeons due to its higher motor control and accuracy delivery of manoeuvres. High-speed surgical drill provides high torque in a small package, making it suitable for a wide range of surgeries such as the spine, neurotology, and ENT procedures.
Regulatory controls are risk-based requirements that apply to medical devices and provide FDA oversight to ensure that medical devices are reasonably safe and effective. Devices in all three classes (Class I, II, and III) are subject to general controls unless exempted by regulations, which require, among other things, that device facilities: register their establishments and list the medical devices they market with FDA; manufacture their devices in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices; label their devices in accordance with labeling regulations; and are not adulterated or misbranded. If a device is exempt from one of the general controls, the classification regulation for that device specifies the exemption. A device facility must register with the FDA and list all of its devices. 510(k) Premarket Notification - Most Class II (moderate risk) devices require FDA 510(k) clearance before they can be legally marketed. Premarket Approval (PMA) - Before a Class III (high-risk) device can be legally marketed, it must first receive Premarket Approval (PMA). Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) provides a potential path to the market for medical devices that may benefit people suffering from rare diseases or conditions. The FDA refers to device software functions as device software functions, which include Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) and Software in a Medical Device (SiMD). The FDA considers software that is intended to be used for one or more medical purposes but is not part of a hardware medical device to be software as a medical device.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
With the growing demand for minimally invasive and non-invasive treatments and an increase in investment and funding for research and development the demand for neurology devices in the US has amped up. The favorable government regulations and reimbursement policies like waivers for certain conditions also encouraged market growth. Companies have expanded their product portfolio to offer a wider range of solutions for surgeons and stakeholders alike which led to investment in research and development to bring innovative products to market. To increase market penetration of Neurology devices, an increase in marketing and promotional efforts to raise awareness and educate customers has been made easy through long-established medical representative channels and medical device distributors. Partnerships with healthcare providers and institutions to offer comprehensive solutions and expand into new geographic markets to increase revenue and market share can be a great strategy for the firms placing their products. Increased healthcare spending and insurance coverage have also led patients to seek more advanced treatments that yield higher health outcomes.
Market Restraints
The major restraints in the neurology device market are:
- Lack of standardized tools to predict the clinical translation of novel medical devices in development, including a lack of in vitro test methods based on human physiology to assess the effectiveness of Neurology electrophysiological devices and the biosafety of emerging device materials.
- There is a lack of a strong regulatory strategy, including biomarkers, for demonstrating performance and evaluating the efficacy of novel devices for early detection and medical intervention in the management of Neurology disorders and injuries.
- There are significant regulatory gaps in the critical evaluation of both recording and stimulating neural interface devices for central and peripheral neural tissue, which impedes long-term adoption due to uncertainty in safe stimulation levels, implant stability, biocompatibility, and device effectiveness.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Medtronic
- Johnson & Johnson
- Boston Scientific
- St. Jude Medical (Acquired by Abbott Laboratories)
- Abbott Laboratories
- GE Healthcare
- Philips Healthcare
- Siemens Healthineers
- B. Braun Melsungen AG
- Zimmer Biomet
Notable Recent Updates
January 2023: APRINOIA Therapeutics which is known for its endeavours in neurodegenerative diseases announced a merger with Ross Acquisition Corp II founded by Wilbur Ross, former US Secretary of Commerce. They are merging at an implied fully diluted transaction equity value of $280 Mn for APRINOIA, with both becoming wholly-owned subsidiaries of the combined company.
December 2022: Human trials for Elon Musk's Neuralink Brain Implant could begin in 2023. The goal is to restore function to people who have suffered brain or spinal cord injuries. Musk stated at a recent Neuralink event that the device's initial applications could include restoring vision to the blind and even allowing paralyzed people to walk again. The idea behind Neuralink is that by connecting to these neurons in our brain, it can interpret and implement messages for us.
April 2022: Synchron, a New York-based company that creates brain-computer interfaces, or BCIs, has received FDA approval to test its brain device in human patients in what is known as an early feasibility study. Stentrode, Synchron's implantable device, is smaller than a matchstick, and unlike its fierce competitor Neuralink, which requires drilling a two-millimeter hole in the patient's skull to install, Stentrode is small enough to be implanted through a blood vessel at the base of the neck and communicates with a second implant in the chest via a tiny wire, and then a transmitter sends signals to an external computer near the patient.
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
Medical devices sold in the United States are subject to the regulatory controls outlined in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) and Title 21-Code of Federal Regulations (21 CFR) Parts 1-58, 800-1299. The regulatory controls and marketing pathways are determined by the device's risk and the regulatory controls required to provide reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness. Premarket Notification (510(k)), De Novo Classification Request, Exempt, Premarket Approval (PMA), Product Development Protocol (PDP), Humanitarian Use Exemption (HDE), and Biologics License Application are the marketing pathways (BLA). The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) is a non-profit organization of medical device regulators from around the world who have banded together to achieve medical device regulatory harmonization. IMDRF creates internationally recognized standards. A 510(k) is required by some class I and most class II devices and the sponsor must demonstrate that the new device is equal in performance to a predicate device in terms of intended use, technological characteristics, and performance testing. A PMA is required for Class III devices which is the most stringent type of premarket submission and before the FDA will grant a PMA, the sponsor must provide valid scientific evidence demonstrating reasonable assurances of safety and effectiveness for the intended use of the device. The De Novo process on the other hand, for a completely new type of medical device, allows for the classification of novel devices for which general controls alone, or general and special controls, provide reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness for the intended use, but for which no legally marketed predicate device exists. HDE establishes a regulatory pathway for class III devices designed to benefit patients suffering from rare diseases or conditions. To be eligible for an HDE, a device must first be designated as a Humanitarian Use Device (HUD), which is obtained through an application to the FDA's Office of Orphan Products Development (OOPD). See Designating Humanitarian Use Device for information on how to request Humanitarian Use Designation (HUD).
Reimbursement Scenario
The FDA is authorized by federal law to charge a fee for a medical device product review. These fees apply to Premarket Notifications (510(k)s), Premarket Approval Applications (PMAs), Product Development Protocols (PDPs), Premarket Reports (PMRs), Panel-Track Supplements, Efficacy Supplements, 180-day Supplements, Real-Time Supplements, 30-Day Notices/135-Day Supplements, Biologics Licensing Applications (BLAs for certain medical devices reviewed by FDA's Centre for Biologics Evaluation and Research), and Requests for Information (513(g)s). Unless the applicant is eligible for a waiver or exemption, the appropriate device user fee must be paid for the above-mentioned applications before FDA can begin its review. To create a Medical Device User Fee Cover Sheet, applicants must first register. To complete the registration process, the organization must provide at least one of the following numbers: Organization Number, Duns and Bradstreet Number (DUNS), and Employer Identification Number (EIN) (EIN), To be responsible for validating users for security purposes, the organization must also identify a Principal Point of Contact (PPOC).
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Device Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Regulatory Landscape for Medical Device
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Type of Medical Device
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Market Size (With Excel and Methodology)
2.2 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Neurology Device Market Segmentation
The Neurology Device Market is segmented as mentioned below:
By Product Type (Revenue, USD Billion):
- Neurostimulation
- Spinal Cord Stimulation Devices
- Deep Brain Stimulation Devices
- Sacral Nerve Stimulation
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation
- Gastric Electric Stimulation
- Interventional Neurology
- Aneurysm Coiling & Embolization
- Embolic Coils
- Flow Diversion Devices
- Liquid Embolic Agents
- Cerebral Balloon Angioplasty & Stenting
- Carotid Artery Stents
- Filter Devices
- Balloon Occlusion Devices
- Neurothrombectomy
- Clot Retriever
- Suction Aspiration Devices
- Snares
- CSF Management
- CSF Shunts
- CSF Drainage
- Neurosurgery Devices
- Ultrasonic Aspirators
- Stereotactic Systems
- Neuroendoscopes
- Aneurysm Clips
By End User (Revenue, USD Billion):
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Specialty Centres
- Others
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.










































