South Africa Dental Care Market Analysis
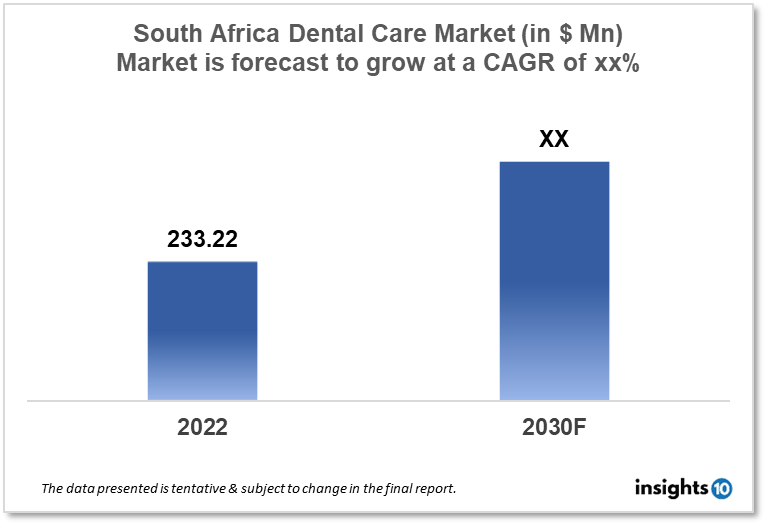
The South Africa Dental Care Market size is at around $233.22 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $xx Mn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of xx% during the forecast period. It was estimated that 12-14% of 35-44-year-olds and 22% of 60-69-year-olds in South Africa had severe periodontal disease, and an estimated 30% of the population in South Africa suffering from the decay of their permanent teeth which causes high demand of dental services that are only forecasted to rise in future. The market is captured by players like Netcare, Medicross, Dental365, and Smile Dental. This report by Insights10 is segmented by treatment type, age group, and clinical setup, and by demography.
Buy Now

South Africa Dental Care Market Executive Summary
The South Africa Dental Care Market size is at around $233.22 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $xx Mn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of xx% during the forecast period. The Department of Health (DoH) administers healthcare in South Africa, although the country lacks a universal healthcare system. It instead employs two parallel systems. A private healthcare system and a public healthcare system work hand in hand. The majority of the population, up to 80%, relies on the public system for health care. The government subsidizes the public system. It is generally underfunded and badly managed. In South Africa, there are about 400 public hospitals. Provincial health agencies oversee large regional hospitals. Municipal governments oversee smaller hospitals and primary care clinics. On the other hand, an estimated 80% of doctors labor in the private sector, treating just around 20% of the population, largely middle and upper-class families and foreigners. As a result, the public system is continually short of resources, but the private system is extremely powerful.
The government of South Africa funds public healthcare through taxation as well as patient point-of-care spending; essential services are subsidized by up to 40%. To govern patient billings and physician compensation, the system employs the Uniform Patient Fee Schedule or UPFS. Patient prices are dependent on income and family size, and the UPFS divides patients into three categories to calculate the cost of various appointments and operations. As a result, consumer out-of-pocket expenditure for these necessary operations has decreased, accounting for only 5.69% of total healthcare spending. Patients who pay in full are either treated by a private physician, are externally supported, or are non-citizens. This applies to foreigners who are allowed to use public facilities but must pay the highest billing category. Patients who are partially subsidized are eligible to have the cost of their care partially paid based on their income. Finally, patients who are totally subsidized are those who are referred to a hospital by Primary Healthcare Services. This usually applies to lower-income individuals. Furthermore, there are times when certain medical services are provided for free.
Periodontal (gum) disease causes swollen, painful, or bleeding gums, as well as poor breath. It is caused by poor oral hygiene, just like dental caries/tooth decay, but it can also be induced by smoking. In severe situations, the teeth might become loose after becoming removed from the mouth and supporting bone. It was estimated that 12-14% of 35-44-year-olds and 22% of 60-69-year-olds in South Africa had severe periodontal (gum) disease, which can lead to tooth loss. Untreated dental caries/tooth decay of permanent teeth is one of the most common disorders worldwide, with an estimated 30% of the population in South Africa suffering from the decay of their permanent teeth. Dental caries/tooth decay occurs when a microbial biofilm (plaque) that forms on the tooth surface transforms free sugars in food and drinks into acids that erode tooth enamel and dentine over time. With a continuing high intake of free sugars, insufficient fluoride exposure, and no regular microbial biofilm removal, tooth structures are destroyed, resulting in cavities and pain, impacts on oral-health-related quality of life, and, in the advanced stage, tooth loss and systemic infection.
South Africa's dental care system is made up of both public and private providers. The state-funded clinics and hospitals provide free basic dental services; however, these facilities are frequently understaffed and underfunded, resulting in long wait times and substandard care. Many South Africans choose to seek treatment at private dental clinics, which provide better care but are more expensive.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
There are several factors that are driving growth in the dental clinic industry in South Africa, including - increasing awareness of oral health and the importance of regular dental check-ups. Rising disposable income and improved access to healthcare financing. Growing demand for cosmetic dentistry procedures such as teeth whitening and veneers. The increasing number of dental insurance schemes and medical aid options available to consumers. The increasing number of dental practitioners in the country includes both local and foreign-trained dentists. Government initiatives to improve access to oral healthcare in underserved areas. Technological advancements in the field of dentistry, such as digital radiography and 3D printing, are making treatments more efficient and cost-effective.
Market Restraints
South Africa's public dental care system is frequently chastised for its lack of accessibility and inadequate services, with many people unable to afford private dental care and unable to access public dental services due to long wait times, a shortage of dental professionals, and insufficient infrastructure. Furthermore, the high expense of dental care in private clinics can make it impossible for some people to obtain critical treatment. As a result, underprivileged communities, particularly those living in rural areas, have a high rate of untreated dental disorders. The government has been attempting to strengthen the public dental care system in recent years by boosting funding and implementing healthcare reform initiatives, but there is still a long way to go to ensure that all South African citizens have access to quality dental treatment. Limited awareness of oral health and the significance of regular dental check-ups among specific population groups, as well as socioeconomic circumstances such as poverty, unemployment, and insufficient education, can all have a negative impact on oral health and limit access to dental care.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Netcare
- Medicross
- Dental365
- Smile Dental
- The Dental Spa
- Oral Health Care
- Dental Solutions
- Smileway Dental
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
The Health Professions Council of South Africa is the governing organization for dental services in South Africa (HPCSA). The Health Professions Act, of 1974 (Act 56 of 1974) established the HPCSA as a statutory authority to regulate the health professions in South Africa. The HPCSA's primary functions and responsibilities include dental practitioner registration, quality assurance, standards of practice, complaints, and disciplinary processes. The HPCSA issues and renews licenses for dental practitioners to practice in South Africa. Through research and innovation, the HPCSA encourages the development and improvement of the dental profession. SAHPRA took over the functions of the Medicines Control Council (MCC) and the Directorate of Radiation Control (DRC), both of which were situated under the National Department of Health (NDoH). As a result, SAHPRA was established as an autonomous agency reporting to the National Minister of Health through its Board. SAHPRA is a National Department of Health body established by the South African government to ensure the health and well-being of humans and animals health.
Reimbursement Scenario
In South Africa, the status of payment for dental services by private insurance companies varies based on the specific insurance plan and the individual's coverage. In South Africa, many private insurance policies cover some dental care, but the degree of coverage varies greatly. Some plans, for example, may just cover routine cleanings and fillings, but others may cover more extensive operations such as orthodontics or oral surgery. In general, dental services in South Africa can be costly, especially for those without insurance. This can be a barrier to access for many people, particularly those with low incomes or who are disadvantaged. Private insurance providers often offer limited coverage options to tourists and expats in South Africa. Tourists and expats in South Africa typically have limited coverage options with private insurance providers, and they may have to pay for dental treatments out of pocket. There are also government-funded healthcare programs in South Africa that provide basic dental treatment, although the quality of care can be poor and there are sometimes substantial wait times for appointments. Companies such as DentalAid offer basic dental insurance for $8.69 per month, while GeoBlue insurance is accessible for foreigners in the US or US citizens abroad. Cigna Global Insurance is a popular choice among expats for dental insurance.
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Service Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Healthcare Services Market in Country
1.6 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Market Size (With Excel and Methodology)
2.2 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Services
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Dental Care Market Segmentation
By Product (Revenue, USD Billion):
In terms of product category, the toothbrush had the highest revenue share (26% in 2020). The rising incidence of cavities, sensitivity, and gingivitis has increased toothpaste usage significantly in both emerging and wealthy countries. As a result, toothpaste is now an essential part of good dental health. In the oral care sector, toothpaste thus commands the biggest market share.
- Toothbrush
- Toothpaste
- Mouthwash
- Dental Floss
- Denture Care
By Age Group (Revenue, USD Billion):
Adults lead the oral care market over the projection period based on age group. The overall expansion of the oral care industry is being driven by adults' increasing consumer knowledge of mouth cleanliness and care. Adult oral care products come in a variety on the market.
- Children
- Adults
- Geriatric
By Sales Channel (Revenue, USD Billion):
The specialty stores dominate the oral care market over the projection period based on the sales channel. Specialty shops carry a broad selection of goods. The employees of specialty businesses provide customers with precise product information. With the aid of specialty shops, customers can also find all types of dental care items under one roof.
- Hypermarkets/Supermarkets
- Specialty Stores
- Drug Stores &Pharmacies
- Convenience Stores
- Online Sales Channel
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.







































