Malaysia Genomics Market Analysis
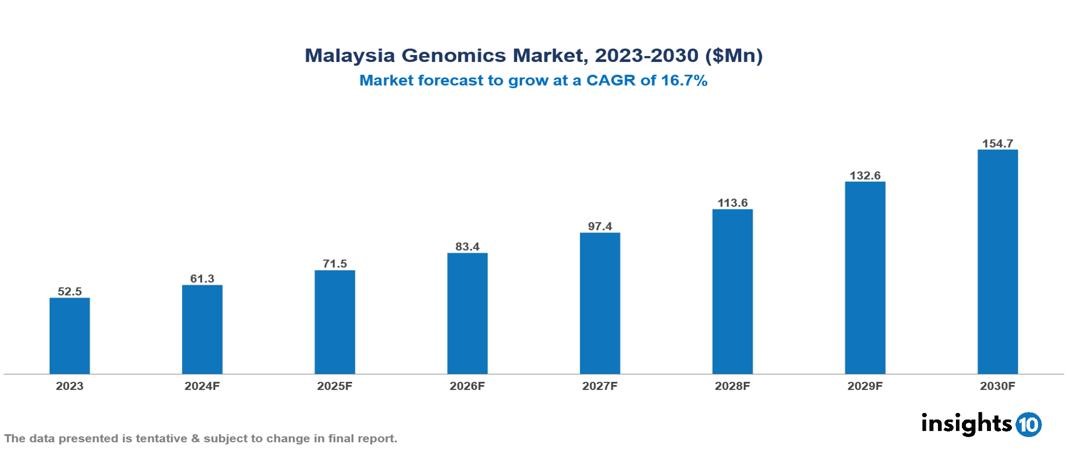
The Malaysia Genomics market was valued at $52.5 Mn in 2023 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 16.70% from 2023 to 2030, to $154.7 Mn by 2030. The key drivers of the market include increasing incidence and prevalence of cancer, the need for advancements in cancer treatments, and the increasing trend of personalized medicines. The prominent players of the Malaysia genomics market are Malaysian Genomics Resource Centre, Codon Genomics, MyTACG Bioscience, Genesis Genome, and Genetics Healthcare Centre, among others.
Buy Now

Malaysia Genomics Market Executive Summary
The Malaysia Genomics market is at around $52.5 Mn in 2023 and is projected to reach $154.7 Mn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 16.70% during the forecast period.
Genomics is the study of an organism's entire genome, including all its genes and how these genes interact with each other and their environment. Genomics incorporates elements of genetics, but is concerned with the characterization of all genes of an organism, rather than individual genes. Genomics attempts to understand all the DNA and genetic material and advance the practical application of that knowledge by relying on a powerful arena of tools such as bioinformatics, microarrays, and Next-generation sequencing (NGS). Genomics has a wide range of applications across various fields. Most importantly, genomics has paved the era for personalized medicine which is transforming the healthcare. Doctors can determine the optimal course of treatment, anticipate a patient’s likelihood of developing certain diseases, and even develop personalized therapies by studying the patient’s genome. Genomics also plays a vital role in disease diagnosis, epidemiology, and treatment. This knowledge helps develop targeted therapies and improve treatment outcomes. Another promising application of genomics lies in the field of pharmacogenomics. By understanding how an individual’s genes influence their response to medications, doctors can prescribe the most effective and safest drugs for them. Lastly, genomics is also beneficial in the biotechnology sector as it is essential for creating new bioproducts, such as biofuels and enzymes. Scientists can modify genes to create organisms that can produce these products more efficiently.
The Malaysia Genomics Markets is therefore driven by significant factors such as the increasing incidence and prevalence of cancer, the need for advancements in cancer treatments, and the increasing trend of personalized medicines. However, the generation and storage of big data, ethical considerations of genomics, high cost associated with genomics, and scarcity of trained professionals restrict the growth and potential of the market.
The prominent players of the Malaysia Genomics Market are Malaysian Genomics Resource Centre, Codon Genomics, MyTACG Bioscience, Genesis Genome, and Genetics Healthcare Centre, among others.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
Increasing incidence and prevalence of Cancer: In Malaysia, in 2020, there were 48,639 new cancer cases reported in Malaysia. By 2040, the incidence of cancer is predicted to double and it is estimated that approximately 1 in every 10 individuals in Malaysia will receive a cancer diagnosis in their lifetime. The rising number of cancer cases fuels the demand for advanced diagnostic tools such as genomic testing. This creates a lucrative market for genomic companies offering such tests and services. Therefore, as the incidence and prevalence of cancer continues to rise, the growth of the genomics market is also expected to grow exponentially.
Needs for advancements in cancer treatment: Due to cancer’s complexity and constant emergence of new mutations, a multifaceted treatment approach is necessary. Genomics provides powerful tools for deeper understanding of cancer paving the way for personalized medicine, early detection techniques, and the development of more effective and potent treatments. Genomics is immensely beneficial as it helps understand the cancer drivers and specific cancer mutations and helps find new therapeutic targets inside cancer cells. Conventional chemotherapy frequently has wide-ranging effects that damage both malignant and healthy cells. However, genomic-based personalized medication presents a more accurate method with possibly fewer negative effects. Pharmaceutical companies can create medications that particularly target the molecular processes involved in the development of cancer by having a thorough understanding of these pathways. This can result in the creation of effective and innovative cancer treatments. Thus, the continuous push for advancements in cancer treatment are significant factors propelling the Malaysia Genomics Market forward.
Increasing trend of personalized medicine: Using genomics, medical professionals can examine a patient’s genome to identify the specific genetic variants associated with the illness. This allows for targeted therapies, which target only the specific mutations or biological mechanisms causing the illness. Personalized medicine provides a more targeted approach with fewer side effects and better therapeutic outcomes than traditional “one-size-fits-all” therapies. Another benefit of genomics is optimized treatment selection. Physicians can forecast a patient’s potential response to various treatment options by knowing their genetic profile. Choosing the best therapy is made possible by this individualized approach, which improves clinical results and leads to faster recovery. Hence, increasing trend of personalized medicine drives the growth of the Malaysia Genomics Market further.
Market Restraints
Generation and storage of big data: Genomic sequencing generates massive amounts of data. Storing, managing, and analysing this data effectively requires robust infrastructure and expertise, which can be expensive for many players. A robust storage infrastructure is necessary for storing genomic data. The massive outputs from DNA sequencing necessitate high-capacity storage systems and thus medical facilities, research institutes, and other organizations required high-capacity storage solutions to house this data. The cost of implementing and maintaining these solutions may be high. Moreover, this volume of data will continue to increase exponentially as the field develops and more genomes are sequenced. It’s possible that the current wave of data growth will outgrow the scalability of existing storage systems, requiring investments in new or upgraded storage technologies. Thus, the massive amount of data that is generated by genomics poses a significant challenge and this can ultimately stifle the growth of the genomics market.
Ethical considerations of Genomics: Preserving people’s genetic privacy is a major concern of genomics. Genetic information is extremely private and can include sensitive details about a person’s origin, health risks, and even characteristics like a predisposition to specific diseases. Misuse or breaches of this data can result in serious consequences Because of this, stringent laws governing data protection and informed permission are essential, but they can also make genetic testing and research more difficult and expensive. Thus, the ethical issues regarding genomics can prevent the genomics market from growing.
High Cost of Genomics: The cost associated with DNA sequencing can be substantial, especially for whole genome sequencing which can limit the accessibility of genomic testing for some patients and research institutions. Also, storing and analysing the vast amounts of data generated by genomics requires powerful bioinformatics tools and software which can be challenging and expensive to purchase and maintain for small-scale companies. Data management systems (DMS), if used, to organize, annotate, and secure genomic data, further adds to the overall cost. Hence, the high cost associated with various aspects of genomics acts as a significant hurdle, hindering the overall growth of the genomics market.
Scarcity of trained professionals: Genomics generates massive amounts of data which requires extensive analysis and thus it demands a skilled workforce with knowledge, expertise, and experience in genetics, bioinformatics, and data processing. The lack of readily available and specialized workforce leads to a bottleneck, hindering the ability to analyse the data effectively into actionable information. Furthermore, the high expense of acquiring and educating these specialists may prevent the industries from recruiting the unskilled individuals. Fewer qualified researchers result in slower progress in developing new genomic technologies, analysing complex genomic data, and unlocking the full potential of this field. Without a skilled workforce to bridge the gap between genomic research and real-world applications, the market growth stagnates and can eventually lead to a decline in the Malaysia Genomics Market.
Regulatory Landscape and Reimbursement Scenario
In Malaysia, the National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA) is the regulatory agency for healthcare products, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and traditional health supplements. The NPRA operates under the Ministry of Health to ensure the efficacy, safety, and quality of healthcare products that are available in the nation.
Before new medications, medical equipment, and herbal health supplements can be sold in Malaysia, the NPRA is responsible for examination and market authorization. Strict quality control procedures are implemented to guarantee that medical supplies fulfil the necessary requirements for both efficacy and safety. This includes conducting quality control methods, maintaining laboratories for product testing, and inspecting production facilities. Overall, the NPRA protects the public health in Malaysia by its rigorous and stringent evaluation and oversight procedures.
Malaysia’s healthcare system offers a mix of public and private options for financing medical care. The government of Malaysia provides a highly subsidized public healthcare system. Citizens and permanent residents can receive basic medical care for little to no cost under this system. Although public hospitals provide high-quality healthcare, waiting period may be longer and access to cutting-edge therapies may be more restricted than in private hospitals. Beyond the services public system offers, private health insurance offers additional coverage. It gives users access to a greater variety of services, such as private medical facilities and clinics, specialist consultations, sophisticated diagnostic techniques and processes, and quicker access to medical services
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Here are some of the major key players in the Malaysia Genomics Market:
- Malaysian Genomics Resource Centre
- Codon Genomics
- MyTACG Bioscience
- Genesis Genome
- Genetics Healthcare Centre
- Orion Biosains
- Illumina
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Danaher Corporation
- Qiagen N.V.
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Service Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Healthcare Services Market in Country
1.6 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Market Size (With Excel and Methodology)
2.2 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Services
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Malaysia Genomics Market Segmentation
By Products and Services
- Consumables and Reagents
- Services
- Instruments, Systems, and Software
By Technology
- Sequencing
- PCR
- Flow Cytometry
- Microarrays
- Other
By Application
- Drug Discovery and Development
- Diagnostics
- Agriculture and Animal research
- Other
By End User
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Academic and Research Institutes
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology companies
- Other
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.