Kenya Genomic Diagnostics Market Analysis
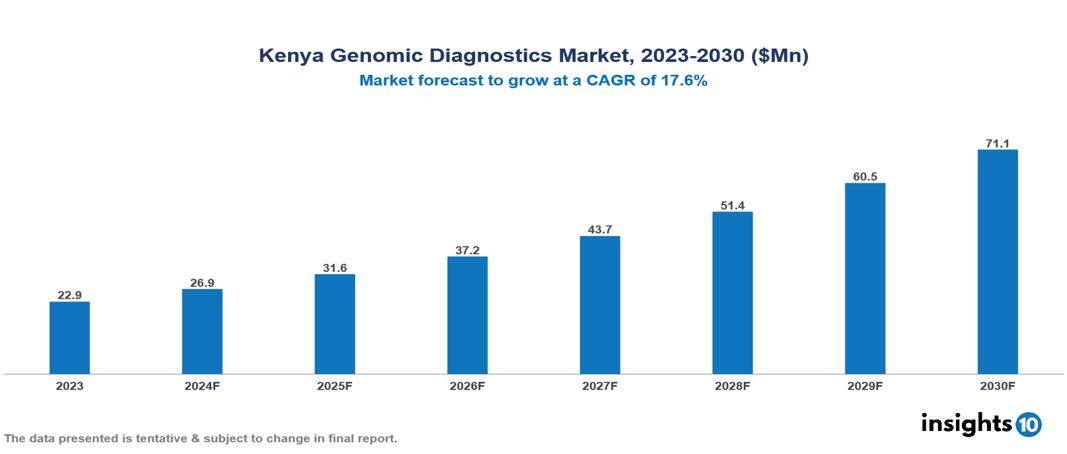
Kenya Genomic Diagnostics Market was valued at $22.86 Mn in 2023 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 17.6% from 2023 to 2030, to $71.09 Mn by 2030. The key drivers of this industry include technological advancements, growing demand for genetic services, and government support and funding. The industry is primarily dominated by Illumina, 23andMe, Myriad Genetics, and Amgen among others.
Buy Now

Kenya Genomic Diagnostics Market Executive Summary
Kenya Genomic Diagnostics Market was valued at $22.86 Mn in 2023 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 17.6% from 2023 to 2030, to $71.09 Mn by 2030.
Genomic diagnostics is a rapidly evolving field that uses an individual's genetic information to diagnose diseases, assess predisposition to future health problems, and guide treatment plans by analyzing DNA or RNA for disease-linked variations. This includes karyotyping to examine chromosome abnormalities, targeted mutation analysis for specific disease-related genes, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) for a comprehensive genetic analysis. Applications encompass disease diagnosis, carrier testing for informed family planning, predictive testing for disease risk assessment, and pharmacogenomics for personalized medication treatments. The benefits of genomic diagnostics include early disease detection, personalized medicine, and improved disease management and prognosis.
In Kenya, the prevalence of chronic diseases is significant, with 25.9% of individuals aged 45 to 69 having risk factors for non-communicable diseases (NCDs) like diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases in 2020. NCDs account for 27% of total deaths and over 50% of hospital admissions, and 28.7% of adults in urban slums experience multimorbidity. The aging population is projected to increase dramatically, with the number of adults aged 60 and older expected to nearly quadruple from 2.57 Mn in 2020 to 10.7 Mn by 2050, leading to increased morbidity and severity of conditions such as Alzheimer’s Disease and cardiovascular diseases.
Market is therefore driven by significant factors like technological advancements, growing demand for genetic services, and government support and funding. However, limited infrastructure and resources, cost and accessibility, and lack of licensed genetic counsellors restrict the growth and potential of the market.
A prominent player in this field is Illumina, which has partnered with AstraZeneca to leverage genomics and AI for faster drug development by identifying new therapeutic targets and biomarkers, 23andMe acquired Lemonaid Health to enhance its personalized healthcare offerings through telehealth and prescription drug delivery services based on genetic information. Other contributors include Myriad Genetics, and Amgen among others.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
Technological Advancements: The advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has dramatically reduced sequencing costs, making it more accessible and affordable for diagnostics in Kenya. High-throughput sequencing technologies have enhanced the speed and accuracy of genetic testing, improving diagnostic capabilities for healthcare providers.
Growing Demand for Genetic Services: There is an increasing demand for genetic testing and counseling services in Kenya, driven by the need to manage heritable diseases such as cancer and sickle cell disease. Rising awareness of the benefits of early diagnosis and medical management is fueling this demand.
Government Support and Funding: The Kenyan government has actively supported genomics research, leading to the establishment of genomic platforms and local capacity development. Increased funding for genomics projects is expected to drive market growth and innovation in Kenya.
Market Restraints
Limited Infrastructure and Resources: Kenya's healthcare infrastructure is still developing, with few well-equipped laboratories and limited resources for genomic research and diagnostics. This lack of infrastructure and trained personnel hampers the widespread adoption of genomics.
Cost and Accessibility: High costs of genetic testing and counseling services remain a significant barrier, especially in rural areas. Limited insurance coverage for these services further restricts access, making it challenging for many Kenyans to benefit from genetic diagnostics.
Lack of Licensed Genetic Counsellors: The absence of licensed genetic counselors in Kenya means patients often receive inconsistent support from managing physicians. This lack of specialized expertise can delay diagnosis and treatment and impact the quality of genetic services.
Regulatory Landscape and Reimbursement Scenario
Kenya is in the process of building its regulatory framework for emerging technologies like genomics. The primary regulatory body involved in the healthcare sector is the Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB), which is responsible for regulating pharmaceuticals and medical devices in Kenya. It plays a crucial role in overseeing the approval and registration of genomic tests. However, given the nascent stage of genomics in Kenya, specific regulations tailored to genomic diagnostics might still be under development.
Reimbursement for genomic diagnostics in Kenya presents significant challenges. The healthcare system is primarily public, with limited resources allocated for advanced diagnostics. The National Hospital Insurance Fund (NHIF) is the primary health insurer, but coverage for genomic tests is likely limited or non-existent. While private health insurance is available, coverage for genomic diagnostics is typically not comprehensive. Consequently, a significant portion of the population relies on out-of-pocket payments for healthcare, making access to genomic diagnostics a considerable challenge.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Here are some of the major key players in the Kenya Genomic Diagnostics
- Illumina, Inc.
- Myriad Genetics, Inc.
- Amgen, Inc.
- 23andMe
- Kenyatta National Hospital (KNH)
- Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI)
- Bioinformatics Institute of Kenya (KIBS)
- Genetic Resources Research Institute (GeRRI)
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Danaher Corporation
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Service Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Healthcare Services Market in Country
1.6 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Market Size (With Excel and Methodology)
2.2 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Services
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Kenya Genomic Diagnostics Market Segmentation
By Technology
- Next Generation Sequencing
- Array Technology
- PCR-based Testing
- FISH
- Others
By Application
- Ancestry & Ethnicity
- Traits Screening
- Genetic Disease Carrier Status
- New Baby Screening
- Health and Wellness-Predisposition/Risk/Tendency
By Product
- Consumables
- Equipment
- Software & Services
By End-user
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Others
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.







































