Kenya Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Analysis
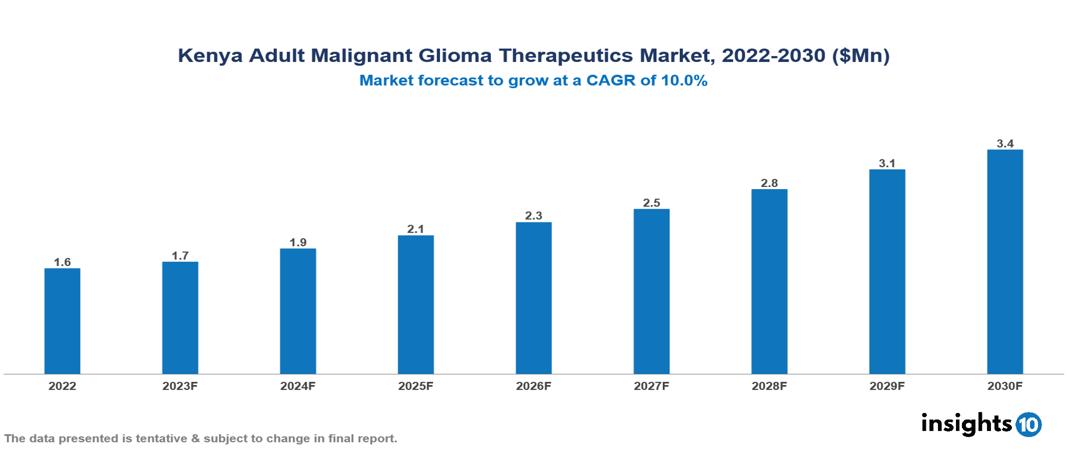
The Kenya Adult Glioma Therapeutics Market is valued at around $2 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $3 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 10% during the forecast period. Growth in the Kenya Adult Malignant Glioma Market is driven by a dynamic combination of factors, including growing awareness of early detection, government funding, increased research for inexpensive medicines, and the impending burden of Glioma. Key players in the Kenya Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market include companies like Roche, Novartis, Merck & Co., Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, M Pharm, Brainlab, Siemens, etc. among others.
Buy Now

Kenya Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Executive Summary
The Kenya Adult Glioma Therapeutics Market is valued at around $2 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $3 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 10% during the forecast period.
Adults who develop malignant glioma are victims of a type of cancer that originates in the brain and spinal cord, particularly in glial cells, which support the nervous system. Anaplastic astrocytoma, anaplastic oligodendroglioma, mixed gliomas, and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most common and severe kind, are the most prevalent types. GBM is a grade IV tumour that grows swiftly and is quite aggressive. Risk factors associated with adult malignant gliomas include age, with an increased incidence in adults, genetic susceptibility, radiation exposure, immune system disorders, and hereditary conditions such neurofibromatosis. Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery are the available treatment options. The prognosis varies based on the kind and grade of the tumour, the goal of the treatment, and the overall health of the patient.
Malignant gliomas represent almost 70% of all brain tumour cases in Kenya, making them the most common histological form of a brain tumour on average. Glioblastoma is the most prevalent kind of glioma in the country occurring in populations with ages above 40 years. Growth in the Kenya Adult Malignant Glioma Market is driven by a dynamic combination of factors, including growing awareness of early detection, government funding, increased research for inexpensive medicines, and the impending burden of Glioma.
Roche is well-positioned to treat gliomas with both cutting-edge, more costly choices and well-established ones like Avastin. One local market participant is M Pharm East Africa. emphasizes cost-effectiveness, enabling a larger patient population to have access to necessary glioma drugs.
Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Improving Research: Kenyan universities, such as the University of Nairobi, are working hard to solve the glioma puzzle. Their efforts are directed on comprehending the distinct genetic and environmental elements that impact the development of gliomas in the Kenyan populace. This localized approach has enormous promise for creating customized treatment plans and, more significantly, for finding accessible and reasonably priced treatments made especially for the environment of the nation.
Enhanced Government Support: The glioma therapeutic market is well-served by the Kenyan government's dedication to enhancing healthcare through programs like Universal Health Coverage. These initiatives, which aim to close the gap in access to necessary healthcare services, might have a positive effect on the market by guaranteeing affordability and fairness in care, especially for underprivileged areas.
Increased Prevalence: Kenya's elderly and expanding populations throw a lengthy shadow that may contribute to a rise in glioma incidence. This is in line with worldwide patterns and emphasizes how urgent it is to look for better and more advanced treatments for malignant glioma.
Market Restraints
Insufficient Coverage: The problem of affordability is made worse by inadequate insurance coverage. Many insurances do not cover the entire range of glioma treatment choices, which leaves patients with severely high out-of-pocket costs. This financial strain may become an impassable barrier, endangering patient outcomes by compromising treatment compliance.
Restricted Government Funding: Glioma research receives little funding from the public and commercial sectors, which starves the pipeline of innovative and reasonably priced treatment alternatives. Due to a lack of financing, patients have few options and high costs for accessible treatments, which stifles innovation and keeps them out of reach.
Lack of Knowledge and Local Stigma: Many patients are discouraged from seeking prompt medical assistance because of the persistent stigma associated with cancer and the lack of public knowledge on the symptoms of gliomas. Delays in diagnosis can have negative effects on treatment outcomes and the window of opportunity for successful intervention. A lot of people don't have thorough knowledge about their available treatments and any possible adverse effects. Their inability to make educated judgments regarding their care is impeded by this information gap, which may result in less adherence and worse-than-ideal treatment selections.
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
Kenya's healthcare system takes the bold path toward Universal Health Coverage (UHC) outlined in the Vision 2030 plan. Service delivery and infrastructure expansion are impeded by insufficient finance. Lack of medical professionals, particularly specialists, especially in rural areas, is the root cause of disparities in access. Many individuals still suffer from out-of-pocket expenses despite the NHIF, and concerns regarding the consistency and efficiency of care in certain public facilities persist. The Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) was established as the Drug Regulatory Authority under the Pharmacy and Poisons Act, Chapter 244 of the Kenyan Laws. The Board is in charge of regulating the production, distribution, and use of poisons and medications, as well as pharmacy practice. The Board aims to put in place the necessary regulatory measures to guarantee the highest standards of safety, efficacy, and quality for all drugs, chemical substances, and medical devices, regardless of whether they are produced locally, imported, exported, distributed, sold, or used. This is done to protect consumers, as intended by Kenya's drug laws.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Roche
- Novartis
- Merck & Co.
- Pfizer
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- AbbVie
- M Pharm
- Brainlab
- Siemens
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Disease Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Patient Journey
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel & Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Kenya Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Segmentation
By Disease Type
- Glioblastoma Multiforme
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma
- Anaplastic Oligoastrocytoma
- Other Types
By Treatment Type
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted Drug Therapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Surgery
- Gene Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Vaccines
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Drug Stores & Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Disease Stage
- Early-Stage Tumour
- Late-Stage Tumour
- Palliative Care
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals
- Speciality Clinics
- Chemotherapy Centres
- Radiotherapy Centres
- Homecare
- Others
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.