Kenya Actinic Keratosis Therapeutic Market Analysis
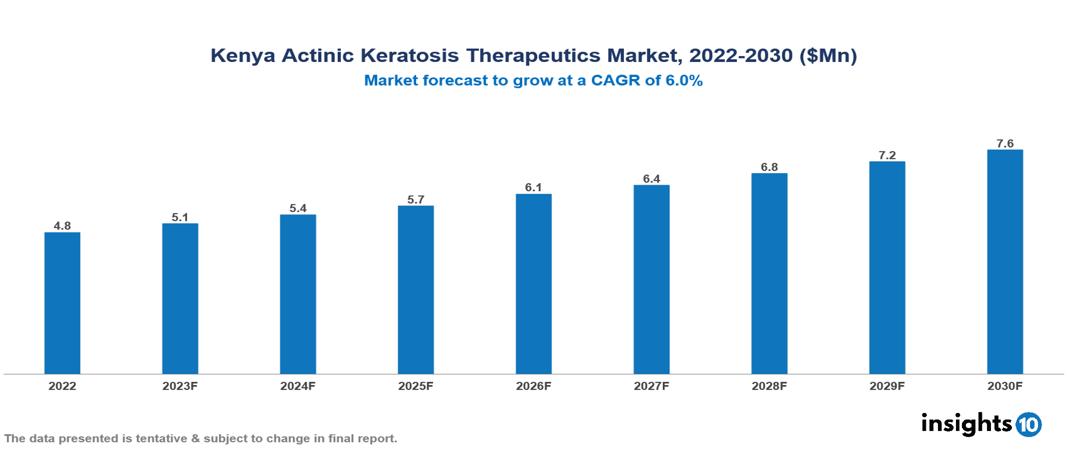
Kenya Actinic Keratosis Therapeutic Market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6% from $5 Mn in 2022 to $8 Mn by 2030. The market is expected to grow as a result of rising prevalence combined with specific environmental variables, a shifting economic landscape, rising disposable incomes, and more access to healthcare services in Kenya. International and local players Galderma, Bayer, Novartis, Mediheal Pharmaceuticals, Mifa, Kepharth etc, contribute to the therapeutic management of Actinic Keratosis
Buy Now

Kenya Actinic Keratosis Therapeutic Market Executive Summary
The Kenya Actinic Keratosis Therapeutic Market is at around US $5 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach US $8 Mn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 6% during the forecast period
Actinic keratosis (AK), also known as solar keratosis, is a scaly, precancerous area that appears on skin damaged by sun exposure. It may be considered a prelude to cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, also known as keratinocyte cancer. Actinic keratoses result from abnormal skin cell development brought on by short-wavelength UVB damage to DNA. They are more likely to appear if you have poor immune function, which can be caused by age, recent sun exposure, underlying disorders, or certain drugs. Seeing a dermatologist is essential for a precise diagnosis and course of therapy. Among the potential treatment options are cryotherapy, laser therapy, topical medications, and surgical removal. In order to reduce the risk of skin cancer and stop the development of AK, it is also essential to adopt sun protection measures such using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing
Kenya, due to its geographical location and lifestyle variables, has a higher prevalence of actinic keratosis (AK) than other areas. In western Kenya, 5.8% of those screened indicated the disease's presence. A high proportion of Kenyans have Fitzpatrick skin types IV and V, which are distinguished by melanin-rich brown to dark brown skin tones. While these skin types provide some natural UV protection, they are nonetheless susceptible to AK, especially after extended and unprotected sun exposure. Growth prospects are anticipated in the Kenya Actinic Keratosis Therapeutic Market due to the increasing number of patients, population aging, technological advancements, and greater accessibility to healthcare. Certain obstacles may need to be addressed, including restricted access to dermatologists and specialized care, differences in the rates of diagnosis and treatment, and the high expense of cutting-edge drugs and procedures
International and local players such as Galderma, Bayer, Novartis, Mediheal Pharmaceuticals, Mifa, Kepharth etc, contribute to the therapeutic management of AK.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
A number of reasons are propelling the Kenya Actinic Keratosis Therapeutics Market's expansion. Growing public awareness of UV exposure and the risk of skin cancer, especially AK, promotes early detection and treatment seeking. Education campaigns by sunscreen manufacturers, public health groups, and physicians help to promote this trend
Years of sun exposure have increased the risk of AK in Kenya's elderly population. This shift in the population is leading to an increase in the number of patients looking for therapeutic and preventative options. In Kenya, increased healthcare costs—particularly those associated with skin conditions like AK—are tied to rising disposable incomes. This trend is also being driven by increased awareness and improved treatment choices
Owing to developments in AK treatment, patients may now have more alternatives and better outcomes. This covers substitutes for light treatment, cryotherapy apparatus, and topical medications such as imiquimod and ingenol mebutate. The use of these more modern technology by healthcare professionals is driving market development
Market Growth Restraints
The Kenya Actinic Keratosis Therapeutic Market is driven by strong forces, but it has constraints that prevent it from reaching its full potential. Even with these improvements, some people still lack access to dermatologists and specialized AK treatment options, particularly in rural and low-income areas. This leads to variations in diagnosis and treatment rates. While generic drugs are readily available, more modern-branded drugs and advanced methods such as light or cryotherapy can be expensive. This may demoralize patients, especially those with little resources or insurance
Even with more information, some people—particularly the elderly or less educated—might not fully understand the risks connected to sun exposure or be able to recognize the symptoms of AK. This might delay the diagnosis and course of treatment. Dermatologists are insufficient in Kenya, especially in rural regions. This limits AK patients' access to professional diagnosis and treatment options
Paying for some AK therapy and comprehending complex insurance plans may be challenging for both patients and medical providers. This might discourage consumers from taking more modern or costly medications. Compared to other developed nations, Kenya could have made fewer investments in the study and development of AK treatments. This can limit the availability of innovative treatment options for the local market
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
Kenya's healthcare system follows the Vision 2030 plan's ambitious route to Universal Health Coverage (UHC). Inadequate funding prevents infrastructure growth and service delivery. Disparities in access arise from shortages of medical personnel, especially specialists, particularly in rural regions. Despite the NHIF, many people still struggle with out-of-pocket costs, and questions about the uniformity and quality of treatment in some public institutions persist. The Pharmacy and Poisons Act, Chapter 244 of the Kenyan Laws, created the Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) as the Drug Regulatory Authority. The Board oversees the manufacture and trade of pharmaceuticals and poisons, as well as the practice of pharmacy. In order to protect consumers as intended by Kenya's drug laws, the Board seeks to implement the necessary regulatory measures to ensure the highest standards of safety, efficacy, and quality for all drugs, chemical substances, and medical devices, whether they are produced locally, imported, exported, distributed, sold, or used.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Galderma
- Bayer
- Novartis
- Mediheal Pharmaceuticals
- Mifa
- Kepharth
- MedicAid International
- Mediworld
- LEO Pharma
- Bausch Health
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Disease Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Patient Journey
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel & Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Kenya Actinic Keratosis Market Segmentation
By Treatment Type
- Topical Treatment
- Procedural Modality
- Photodynamic Therapy
- Others
By Drug Class
- Nucleoside Metabolic Inhibitor
- Immune Response Modifiers
- NSAIDs
- Photo enhancer
- Other Drug Classes
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Drug Stores & Retail Pharmacies
- Online Providers
By Disease Type
- Clinical AK
- Subclinical AK
By End User
- Hospitals
- Private Dermatology Clinics
- Laser Therapy Centres
- Cancer Treatment Centres
- Spas and Rejuvenation Centres
- Homecare
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.