Japan Herbal Supplements Market Report
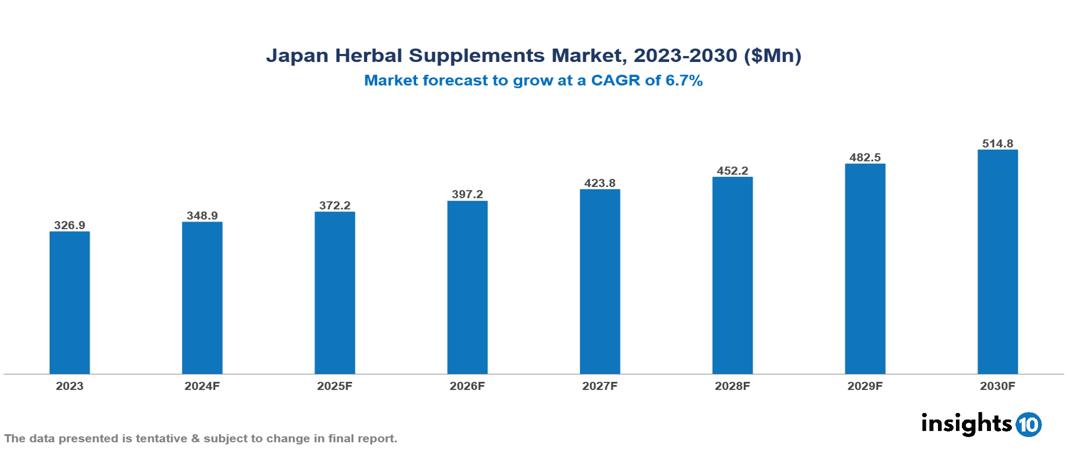
The Japan Herbal Supplements Market was valued at $326.95 Mn in 2023 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2023 to 2030, to $514.80 Mn by 2030. The key drivers of this industry include an aging population, preventive healthcare, and cultural orientation. The industry is primarily dominated by players such as Tsumura & Co, Eisai Co., Ltd, Herbalife, and NOW Foods among others.
Buy Now

Japan Herbal Supplements Market Executive Summary
The Japan Herbal Supplements Market was valued at $326.95 Mn in 2023 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2023 to 2030, to $514.80 Mn by 2030.
Herbal supplements, also known as botanicals, are dietary supplements that contain one or more herbs. These products, which include herbal, botanical, or phytomedicines, are derived from plants or botanicals to promote health or treat illnesses. Herbal supplements are intended specifically for internal use and are commonly available in solid forms such as capsules, pills, tablets, and lozenges, but can also be found in liquid or powder forms. Some popular herbal supplements include Echinacea, Garlic, Ginkgo, Ginseng, St. John's Wort, Saw Palmetto, and Valerian.
In Japan, female consumers are more inclined to use herbal supplements, particularly for weight loss. Active supplement users, who make their own purchasing decisions, are predominantly male, whereas passive users, influenced by others, are more prevalent among females. The market is driven by significant factors like an rising aging population, focus on preventive healthcare, and different cultural orientation. However, distribution challenges, increased competition, and limited scientific evidence restrict the growth and potential of the market.
Prominent players in this field include Tsumura & Co, Eisai Co., Ltd, Herbalife, and NOW Foods among others.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
Rising Aging Population: By 2040, Japan is expected to have 34.8% of its population aged 65 and older, driving demand for herbal supplements as older adults seek natural health solutions to support aging and well-being.
Focus on Preventive Healthcare: Increasing interest in preventive healthcare methods motivates the uptake of herbal supplements for enhancing overall health. This trend acts as a market driver for Japan's herbal supplement industry by promoting consumer demand for natural products that support proactive health management and wellness maintenance.
Different Cultural Orientation: Japan's strong cultural emphasis on wellness and preventive healthcare encourages consumers to prioritize high-quality herbal and dietary supplements. It serves as a significant market driver for Japan's herbal supplement industry, fostering a robust demand for products that support overall well-being.
Market Restraints
Distribution Challenges: Distribution challenges, including logistics complexities and limited networks, hinder efficient access to herbal supplements in Japan, impacting market growth by restricting product availability and consumer accessibility.
Increased Competition: The Japanese market for dietary supplements, including popular products like vitamins, minerals, and probiotics, is firmly established, posing significant competition for herbal supplements in gaining market traction. This competitive landscape acts as a restraint for the herbal supplement market in Japan, potentially limiting their market share and growth compared to more conventional dietary supplements.
Limited Scientific Evidence: The reliance of many herbal supplements in Japan on traditional knowledge and practices, despite their value, is hindered by the ongoing development of robust scientific evidence demonstrating their effectiveness for specific conditions. This lack of strong scientific support may cause some consumers to doubt the efficacy of herbal supplements, thereby restricting market growth.
Regulatory Landscape and Reimbursement Scenario
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), operating under the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW), regulates herbal supplements in Japan. It ensures the safety, quality, and efficacy of these supplements, classifying them based on their intended use as either food with health claims or functional foods. In Japan, herbal supplements typically do not qualify for reimbursement through national health insurance. Classified by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) as either food with health claims or functional foods, herbal supplements are distinct from prescription drugs. While some supplements may offer potential benefits, the MHLW mandates rigorous scientific evidence of their effectiveness before considering them for reimbursement.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Here are some of the major key players in the Japan Herbal Supplement Market:
- Tsumura & Co
- Eisai Co., Ltd
- Herbalife
- NOW Foods
- Amway
- Matsumoto Kiyoshi
- YOTSUBA JAPAN LLC
- KURUMI HERBAL WORKS
- FANCL
- YAMAMOTO
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Product Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Government Regulation in Country
1.6 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel and Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
6. Methodology and Scope
Japan Herbal Supplements Market Segmentation
By Product Form
- Tablet
- Capsule
- Powder
- Others
By Application
- Immunity
- General Wellness
- Specific Health Condition
By Distribution Channel
- Pharmacies
- Supermarket/Hypermarket
- Online
- Specialty Stores
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.









































