Japan Diabetes Drugs Market Analysis
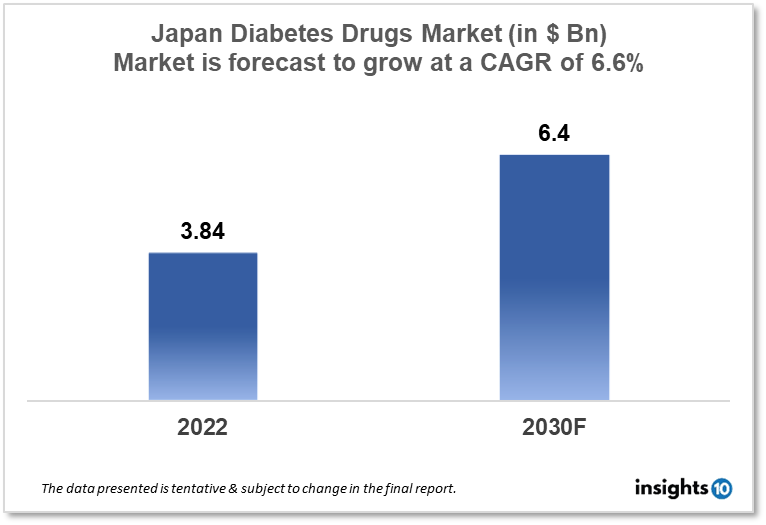
The Japan diabetes drugs market size was valued at $3.84 Bn in 2022 and is estimated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% from 2022 to 2030 and will reach $6.4 Bn in 2030. The market is segmented by drug type, application, and distribution channel. The Japan diabetes drug market will grow because of the Japanese government's initiatives to improve healthcare infrastructure and increase awareness about diabetes management. The key market players are Takeda Pharmaceutical (JPN), Astellas Pharma (JPN), Daiichi Sankyo (JPN), Sumitomo Dainippon (JPN) others.
Buy Now

Japan Diabetes Drugs Market Executive Summary
The Japan diabetes drugs market size was valued at $3.84 Bn in 2022 and is estimated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.6% from 2022 to 2030 and will reach $6.4 Bn in 2030. As of 2021, Japan has the third-largest economy in the world, with a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of approximately $5.2 trillion. Japan has a universal health insurance system that covers almost all of its citizens. The Japanese government spends a significant amount on healthcare, with total health expenditures estimated at 10.9% of its GDP in 2020, which is higher than the average for Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries.
Diabetes is a significant public health concern in Japan, with an estimated 10 Mn people living with the condition. The prevalence of diabetes in Japan has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by factors such as an aging population, changes in diet and lifestyle, and genetic predisposition. The impact of diabetes on the pharmaceutical market in Japan has been significant. The market for diabetes drugs in Japan is one of the largest in the world, with sales exceeding $4 Bn in 2020. The market is expected to continue to grow, driven by an increasing prevalence of diabetes, as well as the availability of new and innovative treatments.
the diabetes drugs market in Japan is attributed to the country's aging population. As people age, their risk of developing diabetes increases, leading to greater demand for diabetes drugs and treatments. Additionally, there has been a shift in dietary habits in Japan, with a greater consumption of high-calorie, high-sugar foods, which can increase the risk of developing diabetes.
The Japanese government has also taken steps to improve the management and treatment of diabetes. In 2016, the government introduced a new system to encourage the use of generic drugs, including diabetes medications, which has helped to reduce costs for both patients and the healthcare system. There has also been a push towards personalized medicine in Japan, with the development of new diabetes drugs and treatments that are tailored to individual patient needs. This has led to the introduction of new medications, such as DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists, which have shown promising results in managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications.
The diabetes prevalence in Japan has had a significant impact on the pharmaceutical market, with the demand for diabetes drugs and treatments expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The development of new and innovative treatments, as well as efforts to improve management and reduce costs, will be key factors in addressing the challenges posed by diabetes in Japan.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers Analysis
The diabetes drugs market in Japan is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of diabetes in the country. Japan has one of the highest rates of diabetes in the world, with approximately 10 Mn people affected by the disease. The growing aging population and adoption of a Westernized lifestyle, including unhealthy eating habits and physical inactivity, are some of the major factors contributing to the rise in diabetes prevalence.
The Japanese government's initiatives to improve healthcare infrastructure and increase awareness about diabetes management have also boosted the demand for diabetes drugs in the country. The government has launched several programs to encourage the early detection and treatment of diabetes, leading to an increase in the adoption of diabetes drugs.
Market Restraints
The high cost of diabetes drugs is a major restraint to the growth of the market in Japan. The Japanese healthcare system is known for its strict price controls on pharmaceuticals, which has resulted in limited access to innovative and expensive diabetes drugs. Moreover, the stringent regulatory environment and complex approval process for new drugs also pose a challenge for companies operating in the Japanese diabetes drugs market.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Takeda Pharmaceutical (JPN)
- Astellas Pharma (JPN)
- Daiichi Sankyo (JPN)
- Sumitomo Dainippon (JPN)
- CSL Limited
- AstraZeneca
- Novo Nordisk
- Sanofi
- Johnson & Johnson
- Abott
- Bayer Pharmaceuticals
- Merck
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Novartis
- GlaxoSmithKline
Notable deals
June 2021, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma entered into a collaboration agreement with Roivant Sciences to develop and commercialize multiple investigational new drugs, including a diabetes drug candidate. The agreement gives Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma exclusive rights to develop and commercialize the drug candidate in Japan and other Asian countries.
April 2021, Sanofi announced the completion of its acquisition of Tidal Therapeutics, a company focused on developing RNA-targeted therapies, including for diabetes. The acquisition will enable Sanofi to expand its drug development capabilities in the area of RNA-targeted therapies and accelerate the development of new treatments for diabetes and other diseases.
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
Policy changes and Reimbursement scenario
In Japan, diabetes drugs are regulated by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), which is responsible for ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of drugs in Japan. The PMDA reviews drug applications and conducts inspections of manufacturing facilities to ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
The regulatory process for diabetes drugs in Japan involves several stages, including pre-clinical studies, clinical trials, and post-marketing surveillance. Drug companies are required to conduct extensive pre-clinical and clinical studies to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their drugs before submitting an application to the PMDA. The PMDA then conducts a review of the application and may request additional data or information before granting approval.
In addition to regulatory approval, diabetes drugs in Japan are subject to price controls set by the Japanese government. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) sets prices for prescription drugs based on a cost-effectiveness assessment, with the aim of ensuring affordable access to essential medicines for the Japanese population. This can result in lower prices for diabetes drugs compared to other countries, but it can also limit the availability of innovative and expensive drugs in Japan.
In Japan, diabetes drugs are included in the national health insurance system, which provides reimbursement for prescription drugs and medical procedures. The system is administered by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare covers the majority of the Japanese population, including both citizens and residents.
Under the National Health Insurance System, patients are responsible for paying a portion of the cost of prescription drugs, known as the co-payment or "patient share." The patient share for prescription drugs varies depending on the drug and the patient's income level, with lower-income patients paying a lower co-payment. The MHLW sets reimbursement prices for prescription drugs based on a cost-effectiveness assessment, with the aim of ensuring affordable access to essential medicines for the Japanese population. This can result in lower prices for diabetes drugs compared to other countries, but it can also limit the availability of innovative and expensive drugs in Japan.
In addition, the MHLW has established a system for providing additional reimbursement for high-cost drugs, including some diabetes drugs. This system, known as the "exceptional high-cost medical care system," provides additional reimbursement for drugs and medical procedures that are deemed necessary but exceed a certain cost threshold.
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Disease Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Patient Journey
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel & Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Diabetes Drugs Market Segmentation
By Drug Type (Revenue, USD Bn):
The drug types considered, in this report include Injectable Drugs and Oral Drugs. Injectable drugs are further classified into insulin-based and non-insulin-based injectables. Oral drugs are further classified into various classes as per their mechanism of action as mentioned below :
- Injectable Drugs
- Insulin Based Injectables
- Non-insulin Based Injectables
- Exenatide (Byetta)
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
- Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy)
- Liraglutide (`Saxenda, Victoza)
- Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)
- Pramlintide (Symlin)
- Tirzepatide (Mounjaro)
- Albiglutide (Tanzeum)
- Oral Drugs
- Biguanides - Metformin (Glucophage and Glucophase XR)
- Sulfonylureas - Glimepiride (Amaryl), Glyburide (DiaBeta), Glipizide (Glucotrol), Gliclazide (Diamicron), Chlorpropamide (Diabinese)
- Meglitinides and D-Phenylalanine Derivatives - Repaglinide (Prandin), Nateglinide (Starlix)
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) - Rosiglitazone (Avandia), Pioglitazone (Actos)
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-4) inhibitors - Sitagliptin (Januvia), Saxagliptin (Onglyza), Linagliptin (Tradjenta), and Alogliptin (Nesina and Vipidia), Teneligliptin (Tenelia), Vildagliptin (Galvus)
- Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitors - Acarbose (Precose), Miglitol (Glyset), Voglibose (Voglib)
- Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors - Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance), Ertugliflozin (Stelgatro)
- Dopamine D2 agonist – Bromocriptine (Parlodel and Cycloset)
- Glucagon like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists - Semaglutide (Rybelsus)
- Bile Acid Sequestrants (BASs) - Colesevelam (Welchol)
- Others (Fixed Dose Combination Drugs)
By Application (Revenue, USD Bn):
Based on application, the market is segmented into Type 1 and Type 2. The 2 types of diabetes drugs are segmented and dominate the market. The Type 2 diabetes segment accounts for the largest sales of the worldwide market a few different kinds. The excessive prevalence of type 2 because of sedentary lifestyles and obesity in all age groups is attributed to the current situation. Around 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1, and approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes in UK are type 2. Hence, it is estimated to the diabetes drugs market will grow across the globe during the forecast period.
- Type 1 diabetes (due to β-cell destruction, usually leading to absolute insulin deficiency)
- Type 2 diabetes (due to a progressive insulin secretory defect on the background of insulin resistance)
- Other diabetes types
By Distribution Channel (Revenue, USD Bn):
Based on distribution channels, the market is classified into hospital pharmacies, rental pharmacies, and online pharmacies. The hospital pharmacies captured the highest market share, owing to the availability of trained & qualified personnel and favorable reimbursement structure. Online pharmacies are estimated to register the highest CAGR in the forecast period, it is attributed to the technological adaptation and acceptance of online pharmacies. Retail pharmacies showed a moderate market share improvement in the healthcare facilities in developing countries is anticipated to propel the popularity of retail pharmacies during the forecast period.
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Retail Pharmacy
- Online Pharmacy
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.







































