Japan Alcohol Addiction Therapeutics Market Analysis
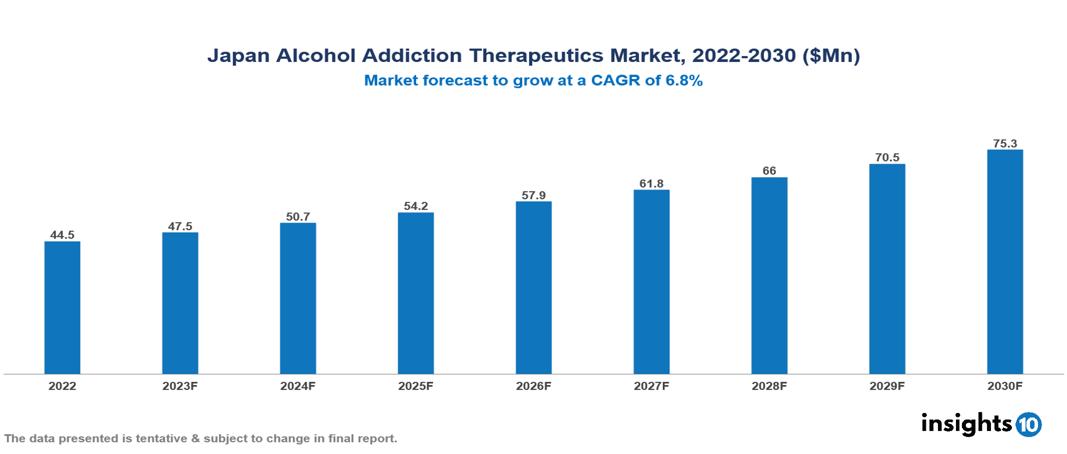
The Japan Alcohol Addiction Therapeutics Market is valued at around $44 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $75 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period. Japan's market growth is propelled by government acknowledgment, increased mental health funding, and a rising demand for more effective and tolerable novel therapies to address the challenges posed by alcohol misuse in an aging population. The key players involved in the research, development, and distribution of Alcohol Addiction Therapeutics in Japan are Lundbeck, AstraZeneca, Alkermes, Merck & Co., TEVA Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, BioCorRx, Otsuka, Kyorin, Eisai etc among others.
Buy Now

Japan Alcohol Addiction Therapeutics Market Executive Summary
The Japan Alcohol Addiction Therapeutics Market is valued at around $44 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $75 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period.
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is a complex and diverse condition characterized by dysregulation of several executive function-related brain circuits, resulting in excessive alcohol consumption despite negative consequences for one's health and social life, as well as withdrawal symptoms when alcohol access is restricted. Anyone may get AUD, regardless of age, gender, or background. AUD may have a significant impact on someone's health, relationships, and overall quality of life. Treatment options include both psychological and pharmacological therapies aimed at reducing alcohol use and/or encouraging sobriety, as well as addressing dysfunctional behaviours and impaired functioning. Psychological therapies for AUD include cognitive behavioural therapy, motivational interviewing, and contingency management. Medications used for the treatment of AUD include disulfiram, acamprosate, naltrexone, and nalmefene.
Around 12-15% of the Japanese population who are 20 or older consume alcohol at amounts that are deemed dangerous or hazardous. This corresponds to around 18 million people in the country, making this a major issue. Japan's market growth is propelled by government acknowledgment, increased mental health funding, and a rising demand for more effective and tolerable novel therapies to address the challenges posed by alcohol misuse in an aging population.
Otsuka Pharmaceutical and Kyorin Pharmaceutical are projected to have a greater market share due to their long-standing involvement in the Japanese CNS market and established medicines such as acamprosate and naltrexone. Among the foreign players, Alkermes' Vivitrol and naltrexone have a considerable share, whereas Lundbeck's Selincro may have a lower proportion due to its recent debut.
Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
Ageing Population: Japan's increasingly aging population raises worries about the health consequences of alcohol misuse, such as liver cirrhosis and mental health disorders. The government's emphasis on enhancing aged healthcare services, particularly increasing mental health funding, fosters the research and implementation of AUD treatments.
Government Support: The Japanese government's "Basic Policy on Mental Health and Welfare" (2012) acknowledges AUD as a serious public health concern and highlights the importance of comprehensive treatment programs. Policy improvements aiming at expanding access to mental health treatments, including coverage for AUD treatment through the national health insurance program, are expected to fuel market expansion.
Rising Demand for Novel Therapies: Existing drugs, such as naltrexone and acamprosate, nevertheless lack efficacy, tolerability, and long-term effectiveness, leading to increased need for novel therapies. The discovery of novel drugs with distinct mechanisms of action, such as disulfiram-based implants and glutamate-modulator drugs, offers great promise for market expansion.
Market Restraints
Social Stigma and Lack of Knowledge: The stigma associated with mental health difficulties and AUD in Japanese society hinders people from seeking help, resulting in a gap between existing needs and treatment usage. Traditional cultural beliefs that promote self-reliance and social conformity might further discourage people from seeking professional aid. Lack of knowledge about available treatment choices or the efficacy of medication-assisted treatment adds to low treatment rates.
System Complexity: Japan's fragmented healthcare system, which separates medical and mental health care, might hinder access to comprehensive AUD treatment. The scarcity of qualified mental health specialists specializing in AUD therapy, particularly in rural locations, poses access hurdles. Reimbursement policies within the national health insurance program may not cover all AUD treatment choices, posing financial challenges for patients.
Regulatory Barriers and Treatment Modalities: In comparison to other markets, Japan's stringent regulatory processes for authorizing new pharmaceuticals might cause the launch of potentially effective remedies to be delayed. Some elements of the healthcare system and patients may choose non-pharmacological methods like psychotherapy, which may restrict the acceptability of medication-assisted treatment.
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
Japan’s statutory health insurance system provides universal coverage. It is funded primarily by taxes and individual contributions. Enrollment in either an employment-based or a residence-based health insurance plan is required. Benefits include hospital, primary, specialty, and mental health care, as well as prescription drugs. The national and local governments are required by law to ensure a system that efficiently provides good-quality medical care. The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) is the government organization in charge of reviewing drugs and medical devices, overseeing post-market safety, and providing relief for adverse health effects. The PMDA operates under the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW). These two government organizations both handle a wide range of activities, from approval reviews to post-market surveillance.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Lundbeck
- AstraZeneca
- Alkermes
- Merck & Co.
- TEVA Pharmaceuticals
- Pfizer
- BioCorRx
- Otsuka
- Kyorin
- Eisai
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Disease Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Patient Journey
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel & Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Japan Alcohol Addiction Therapeutics Market Segmentation
By Therapy Type
- Pharmacological Therapy
- Behavioural Therapy
- Digital Health Interventions
- Others
By Disease Stage
- Mild Alcohol Dependence
- Moderate Alcohol Dependence
- Severe Alcohol Dependence
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Topical
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Drug Stores & Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By End User
- In-Patient Centres
- Out-Patient Speciality Clinics
- Residential Treatment Centres
- Homecare
- Others
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.