Japan Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Analysis
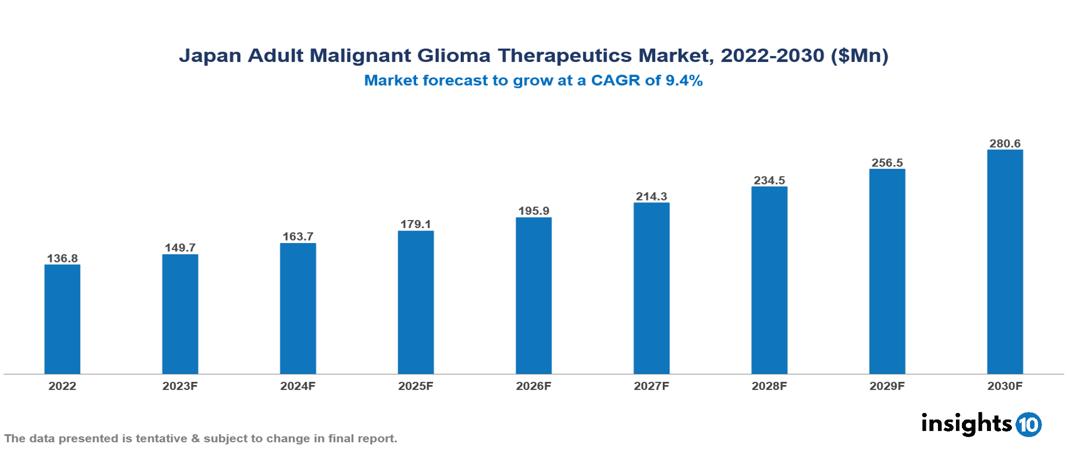
The Japan Adult Glioma Therapeutics Market is valued at around $137 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $281 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period. A progressive healthcare system, active involvement in clinical research, increasing patient awareness, and cooperative efforts amongst pharmaceutical firms are all contributing factors to the growth of the Japan Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market. Key players in the Japan Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market include companies like Roche, Novartis, Merck & Co., Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, Chugai Pharmaceuticals, Taiho Pharmaceuticals, and Novocure etc.
Buy Now

Japan Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Executive Summary
The Japan Adult Glioma Therapeutics Market is valued at around $137 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $281 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period.
Adult Malignant Glioma is a type of brain tumor caused by glial cells, which support neurons and aid in the functioning of the central nervous system. They can be categorized into various subtypes based on their origin and microscopic appearance, with the primary forms being Astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas. Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive type of Astrocytoma. Recent advancements in glioma treatment include the use of various strategies such as targeted therapy, virotherapy, and the potential discovery of new medications. Virotherapy, which involves the use of genetically modified viruses to target tumour cells, has shown promise in the treatment of gliomas. Treatment options for gliomas include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surgery. Targeted treatments, such as Vorasidenib, have demonstrated potential in slowing the growth of gliomas.
Overall, 14.1 (11.6 for men and 16.4 for women) brain tumours per 100,000 people were reported to occur in Japan each year, accounting for age-adjusted incidence. Brain tumours classified as malignant are most frequently Gliomas. In Japan, the 5-year overall survival rate for GBM is still less than 10%, despite the fact that they are uncommon malignancies with a better prognosis for grade II/III gliomas during the past 40 years. Few chemotherapeutic medicines are available to treat gliomas, which contributes to their continued poor prognosis.
A progressive healthcare system, active involvement in clinical research, increasing patient awareness, and cooperative efforts amongst pharmaceutical firms are all contributing factors to the growth of the Japan Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market.
The first line of treatment for glioma has traditionally been a combination of Temozolomide ( by Merck) and Avastin (by Roche). With its own Temozolomide formulation and engagement in the development of new glioma treatments, Esai has recently emerged as a strong player in the local market, demonstrating that investing in cutting-edge glioma medicines paves the way for future success.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
Changing Treatment Context and Personalized Medicine: New treatments for gliomas, such as checkpoint inhibitors and targeted medications, are revolutionizing the field. Furthermore, the increasing focus on customized medicine—which takes into account unique genetic characteristics and tumour profiles—opens the door to more focused and successful treatment approaches.
Growth in Patient Awareness and Advocacy: Patient advocacy organizations are essential for empowering patients and influencing research goals as knowledge about gliomas and their treatment choices increases. By speaking together, we can make sure that patient demands are at the forefront of market innovation.
Collaborative Efforts and Knowledge Sharing: Collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare providers are encouraging the exchange of information and accelerating the development of innovative glioma treatments. This motivation is further strengthened by the collaborative culture seen throughout the Japanese healthcare system. The rapidly developing field of medical technology is driving improvements in glioma diagnosis and treatment options. Japan offers optimism for future breakthroughs by actively participating in several clinical studies investigating potential new medicines.
Market Restraints
Exorbitant Treatment Expenses and Unequal Access: For many Japanese patients, particularly those without insurance, the high cost of innovative glioma treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted medications, can be a major obstacle. This raises questions about how unequal access to potentially transformative therapies might exacerbate already-existing healthcare inequities. To guarantee equal access, addressing affordability through creative pricing strategies and increasing insurance coverage will be essential.
Regulatory Obstacles and Protracted Approval Procedures: Getting innovative medicines approved in Japan's strict regulatory environment may be a difficult and drawn-out procedure. This may affect the prognosis and quality of life of patients by delaying the provision of novel medicines to those in urgent need. Simplifying the approval procedure without sacrificing strict safety requirements can be a major advancement.
Lack of Knowledge: Not many people are using the latest therapy choices as they are very expensive. There fails to be much information available, and there are no noticeable indicators of improved efficacy with those options. As a result, there is little knowledge or experience about these choices among patients and healthcare professionals, which ultimately results in a low demand for them.
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
The national health insurance system in Japan is statutory. The main sources of funding for it are individual contributions and taxes. Enrollment in a health insurance plan by job or domicile is a prerequisite. Prescription medications and hospital, general, specialized, and mental health care are included in the benefits package. Laws mandate that both national and local governments maintain an effective system for delivering high-quality healthcare. The government agency in charge of monitoring post-market safety, compensating for unfavourable health consequences, and evaluating medications and medical devices is called the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA). The Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW) oversees the PMDA's operations. These two government agencies deal with a variety of tasks, such as post-market surveillance and approval evaluations.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Roche
- Novartis
- Merck & Co.
- Pfizer
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Eisai
- Otsuka Pharmaceuticals
- Chugai Pharmaceuticals
- Taiho Pharmaceuticals
- Novocure
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Disease Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Patient Journey
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel & Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Japan Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Segmentation
By Disease Type
- Glioblastoma Multiforme
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma
- Anaplastic Oligoastrocytoma
- Other Types
By Treatment Type
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted Drug Therapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Surgery
- Gene Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Vaccines
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Drug Stores & Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals
- Speciality Clinics
- Chemotherapy Centres
- Radiotherapy Centres
- Homecare
- Others
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.