Indonesia Pharmacy Automation Device Market Analysis
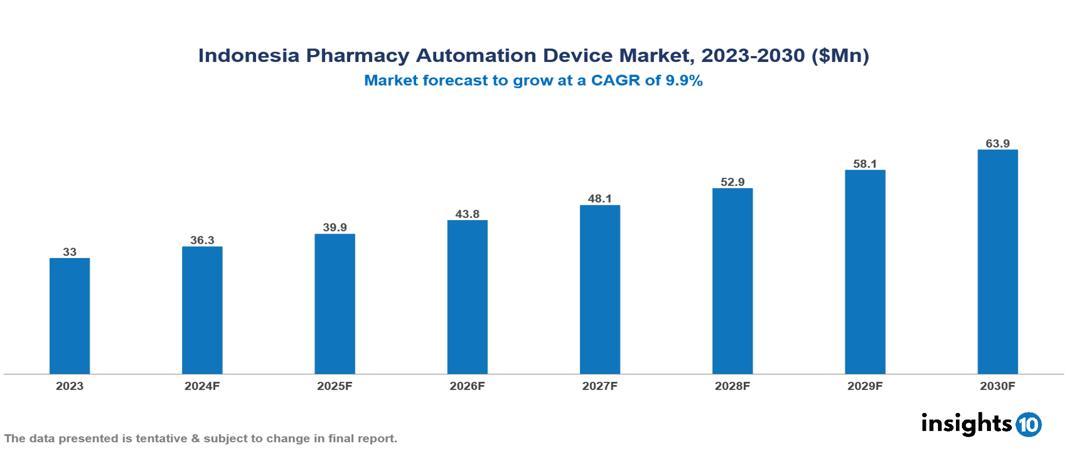
The Indonesia Pharmacy Automation Device Market was valued at $33 Mn in 2023 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 9.9% from 2023 to 2030, to $63.9 Mn by 2030. Indonesia Pharmacy Automation Device Market is growing due to Increasing Healthcare Expenditure, Adoption of Electronic Health Records, and Advancing Technology. The market is primarily dominated by players such as Touchpoint Medical, Swisslog Healthcare, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd, Fanuc Corporation, Kuka Ag, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Amerisource Bergen Corporation, Accu-Chart Plus Healthcare Systems, Omnicell, Inc.
Buy Now

Indonesia Pharmacy Automation Device Market Executive Summary
Indonesia Pharmacy Automation Device Market is at around $33 Mn in 2023 and is projected to reach $63.9 Mn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.9% during the forecast period.
The Pharmacy Automation market is a subset of the larger E-Healthcare industry. It focuses on the automation of pharmacy processes, such as the filling of prescriptions, inventory management, and drug dispensing. Automation of these processes can help reduce costs, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency. It can also help reduce the risk of medication errors, which can have serious consequences for patients. For this reason, the pharmacy automation system plays a crucial role in reducing errors related to storage, inventory, usage, and retrieval. Pharmacy automation is a perfectly acceptable and helpful way to improve the accuracy and efficiency of pharmacies.
The penetration rate of pharmacy automation devices in Indonesia has been steadily increasing, with a notable impact on efficiency and effectiveness in healthcare settings. These devices have been shown to improve operational efficiency by up to 30% and enhance medication error reduction by 50%. Several companies, including global players like BD (Becton, Dickinson, and Company) and local startups such as PT Prodia Widyahusada, have entered the Indonesian market with innovative automation solutions. Startups like PT Kinetic Mitra Solusi are also contributing to the growth by developing advanced robotics and software solutions tailored to local pharmacy needs. The market, therefore, is driven by significant factors like Increasing Healthcare Expenditure, Adoption of Electronic Health Records, and Advancing Technology. However, High Costs, Security Concerns, Complexity, and Integration Issues restrict the growth and potential of the market.
Becton, Dickinson, and Company, in collaboration with Frazier Healthcare Partners, finalized the acquisition of Parata Systems for $ 1.525 Bn.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
Increasing Healthcare Expenditure: Healthcare spending has been expanding gradually, with governmental and private sector investments driving the sector's expenditures, which are expected to account for 4.2% of GDP in 2023. A greater emphasis is being placed on increasing efficiency and cutting costs as the healthcare system grows to accommodate the demands of an expanding population. By minimizing errors, improving inventory control, and expediting the pharmaceutical dispensing process, pharmacy automation systems are essential to reaching these objectives. In addition to improving patient safety and satisfaction, this efficiency enables pharmacies to run more profitably in a cutthroat industry.
Adoption of Electronic Health Records: The increasing use of electronic health records and the proactive efforts of the government to encourage the implementation of pharmacy automation systems have propelled the market. The innate expansion of these systems and, by extension, the market as a whole is being propelled by the rising demand for high-quality healthcare and the growing awareness of the advantages of automation systems. The market's stability and future growth prospects are bolstered by this regulatory assistance.
Advancing Technology: Modern pharmacy automation systems are becoming more and more common, and the pharmaceutical industry is benefiting from these technical developments. Automated robotic systems are now installed in more than 30% of pharmacies in affluent nations. To improve medication management accuracy and operational efficiency, these gadgets incorporate state-of-the-art technology including IoT connectivity, robotics, and AI-driven software. Pharmacies can satisfy the rising demands for quality and safety in healthcare delivery, retain their competitiveness, and adhere to regulatory requirements by utilizing these technologies.
Market Restraints
High Cost: Pharmacy automation has several advantages, however the initial expenditures may be a significant barrier. Installing these devices can cost anywhere between $150,000 and $500,000. Smaller pharmacies with tighter resources may find this difficult to bear. The long-term expense is increased by upkeep and upgrades, thus the cost doesn't end there. This hefty upfront cost may act as a significant deterrent, causing adoption to lag. The expense of automation may be prohibitive in places with limited healthcare resources, which would further restrict its adoption.
Security Concerns: Pharmacy automation offers a double-edged sword. While it streamlines operations, the devices themselves become targets for cyberattacks. With nearly half of healthcare organizations already hit by cyberattacks on medical devices, pharmacies have a valid concern about protecting sensitive patient data. Strong security is essential to prevent breaches, but it comes at a cost. Implementing and maintaining robust safeguards can be expensive and require dedicated resources, which might discourage pharmacies, especially those with limited cybersecurity capabilities. These security worries can put the brakes on adopting automation altogether.
Complexity and Integration Issues: Electronic health records (EHRs) and pharmacy management systems can be difficult and time-consuming to integrate with integrated pharmacy automation systems. Compatibility and smooth data interchange between many systems must be ensured, which leads to this complexity. Survey results really show that 60% of pharmacies have trouble incorporating new technology into their current workflows. There could be problems with daily operations if many pharmacies don't have the technological know-how needed for these kinds of interfaces. Prescribers may also be reluctant to use automation technology due to concerns about operational disruptions or system failures during the integration phase. Increased operational complexity derives from the difficulty of managing and maintaining these interconnected systems, which could prevent their widespread adoption.
Regulatory Landscape
In Indonesia, the regulatory landscape for pharmacy automation devices is evolving with a focus on enhancing healthcare efficiency and patient safety. The market for these devices, encompassing automated dispensing systems, robotic prescription dispensers, and medication management systems, is driven by increasing healthcare demands and advancements in technology. Regulatory authorities like the National Agency of Drug and Food Control (BPOM) play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with safety standards and operational protocols for these devices. As the healthcare sector continues to modernize, there is growing emphasis on the adoption of automated solutions to streamline workflows, minimize errors, and improve overall patient care across Indonesian pharmacies.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Here are some of the major key players in Indonesia Pharmacy Automation Device Market:
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Touchpoint Medical
- Swisslog Healthcare
- Fanuc Corporation
- Kuka Ag
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Amerisource Bergen Corporation
- Accu-Chart Plus Healthcare Systems, Inc.
- Omnicell, Inc.
- McKesson Corporation
- Pearson Medical Technologies
- Baxter
- Talyst, LLC
- Scriptpro LLC
- Becton Dickinson and Company
- Fulcrum Pharmacy Management, Inc.
- Medacist Solutions Group, LLC
- Aesynt, Inc
- Capsa Healthcare
- Cerner Oracle
- ARxIUM
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Device Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Regulatory Landscape for Medical Device
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Type of Medical Device
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Market Size (With Excel and Methodology)
2.2 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Indonesia Pharmacy Automation Device Market Segmentation
Based on Product
- Automated Medication Dispensing Systems
- Automated Packaging and Labeling Systems
- Automated Table-Top Counters
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems
- Other Pharmacy Automation Systems
Based on Pharmacy Type
- Independent
- Chain
- Federal
Based on Pharmacy Size
- Large Size Pharmacy
- Medium Size Pharmacy
- Small Size Pharmacy
Based on Application
- Drug Dispensing and Packaging
- Drug Storage
- Inventory Management
Based on End-user
- Retail Pharmacy
- Inpatient Pharmacies
- Outpatient Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacy
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.







































