Indonesia Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Analysis
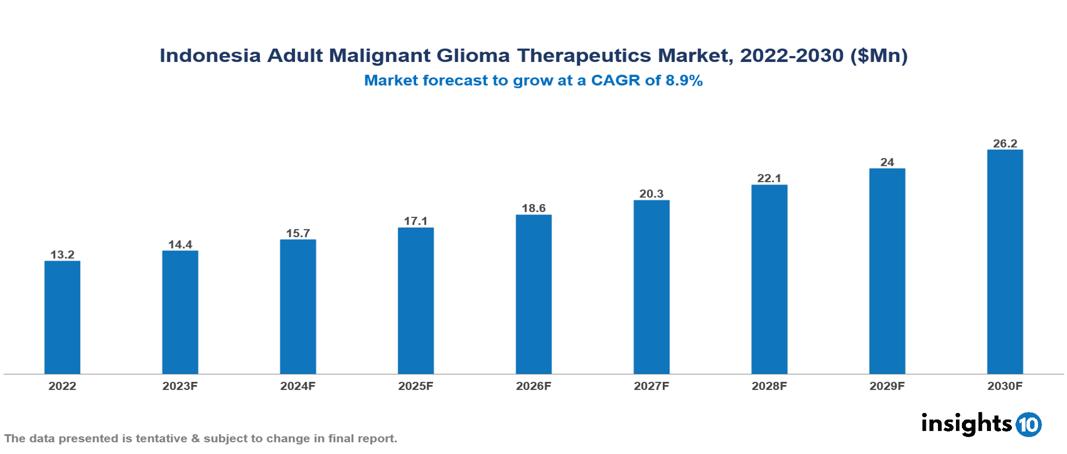
The Indonesia Adult Glioma Therapeutics Market is valued at around $13 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $26 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period. The UHC program of the Indonesian government, together with the nation's expanding economic might and a rise in domestic investment and research projects, is greatly boosting the manufacture of generic drugs domestically and encouraging the development of diagnostic and therapeutic technologies. Key players in the Indonesia Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market include companies like Roche, Novartis, Merck & Co., Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kalbe Farma, Stryker, Elekta, Siemens, etc among others
Buy Now

Indonesia Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Executive Summary
The Indonesia Adult Glioma Therapeutics Market is valued at around $13 Mn in 2022 and is projected to reach $26 Mn by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period.
Adult Malignant Glioma is a form of brain tumour caused by glial cells, which support neurons and assist the function of the central nervous system. Based on the cells from which they originate and how they look under the microscope, they may be divided into several subtypes. Astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas are the three primary forms of gliomas. Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) is a type of astrocytoma, which is the most dangerous form. Treatment for gliomas has advanced recently using a variety of strategies, including targeted therapy, virotherapy, and the discovery of possible novel medications. Glioma treatment options such as virotherapy, which utilizes genetically engineered viruses to attack tumour cells, have shown promise. Gliomas can be treated with radiation treatment, chemotherapy, and surgery. Drugs used in targeted treatment, such as Vorasidenib, have shown promise in slowing the growth of gliomas.
Among the countries of Southeast Asia, Indonesia has a noticeably greater rate of primary brain tumours, including gliomas. There can be geographical differences in the frequency of gliomas in various regions of the country. In Indonesia, GBM is still the most frequent kind of glioma. The UHC program of the Indonesian government, together with the nation's expanding economic might and a rise in domestic investment and research projects, is greatly boosting the manufacture of generic drugs domestically and encouraging the development of diagnostic and therapeutic technologies.
Certain sectors, such as first-line chemotherapy, are dominated by multinational giants. Temozolomide from Roche and Bevacizumab, an anti-angiogenic treatment medication from Novartis are two such dominant players in the Indonesia Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market. Locally made generic versions of chemotherapeutic medications, such as those offered by Kalbe Farma, are becoming more and more popular and giving patients more affordable treatment alternatives.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
Government Initiatives: BPJS Kesehatan, the Indonesian government's initiative for Universal Health Coverage (JKN), is a major factor in increasing access to cancer treatment and other healthcare services. This program makes treatment more accessible to a larger population by covering necessary chemotherapy medications like bevacizumab and temozolomide. Government programs encouraging the local manufacture of generic medications may also spur market expansion since they reduce treatment costs and increase accessibility for the general public.
Growing Economic Power: The growing middle class in Indonesia has more disposable income, which increases their willingness to spend on medical care, including glioma treatment. This results in a need for both cutting-edge, expensive medicines and reasonably priced generic drugs.
Increasing Local Research & Investment Initiatives: Access to cutting-edge diagnostic and therapeutic technologies is being improved by large investments made throughout Indonesia in cancer centers and specialty hospitals. Additionally, organizations like Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital and the National Cancer Institute of Indonesia are actively engaged in clinical studies for novel glioma medicines. The goal of these initiatives is to create treatment choices that are accessible and cheap, specifically catered to the requirements of Indonesian citizens.
Market Restraints
Unequal Allocation of Healthcare Resources and Expertise: The majority of modern treatment facilities, such as cancer centers and specialist oncologists, are primarily located in metropolitan regions, leaving rural communities underserved. This regional difference poses serious challenges to prompt diagnosis, the start of treatment, and access to quality care. The lack of qualified healthcare workers makes this access gap even worse.
Regulatory Hurdles and Market Access Issues: Difficult and drawn-out regulatory procedures for bringing new medications to the Indonesian market may cause patients to miss out on cutting-edge treatments. Pharmacies may be deterred from joining the market by onerous regulations and bureaucratic processes, which would reduce the number of available treatments. Counterfeit pharmaceuticals can also jeopardize patient safety and reduce the effectiveness of treatment.
Public Knowledge and Stigma: A lack of knowledge regarding gliomas, their symptoms, and available treatments might cause people to put off getting a diagnosis and be reluctant to seek medical attention. Cancer sufferers are further deterred from coming forward and seeking accessible care by the societal stigma attached to the disease. These problems may serve as market barriers.
Healthcare Policies and Regulatory Landscape
Indonesia's Universal Health Coverage Program (JKN) is a comprehensive endeavour that strives to provide equal access to basic healthcare services. JKN uses the required insurance payments to pay for a wide range of services, including cancer treatment. Notably, Indonesia emphasizes primary care and the integration of traditional medicine while empowering local governments through its decentralized structure. Prioritizing prevention and early diagnosis is key to addressing pervasive issues such as inadequate funding for JKN, unequal access in urban and rural regions, and a scarcity of healthcare workers. The National Agency for Drug and Food Control (BPOM) is the highest authority on drug control. BPOM protects medication costs and safety using a variety of measures, including quality control, manufacturing monitoring, registration, and price controls. Protracted registration procedures, administrative roadblocks, and changing rules frequently test the endurance of pharmaceutical companies.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- Roche
- Novartis
- Merck & Co.
- Pfizer
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Kalbe Farma
- Stryker
- Elekta
- Siemens
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Disease Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Patient Journey
1.6 Health Insurance Coverage in Country
1.7 Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)
1.8 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Epidemiology of Disease
2.2 Market Size (With Excel & Methodology)
2.3 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Diagnosis
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Indonesia Adult Malignant Glioma Therapeutics Market Segmentation
By Disease Type
- Glioblastoma Multiforme
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
- Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma
- Anaplastic Oligoastrocytoma
- Other Types
By Treatment Type
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted Drug Therapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Surgery
- Gene Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Vaccines
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Drug Stores & Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Disease Stage
- Early-Stage Tumour
- Late-Stage Tumour
- Palliative Care
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals
- Speciality Clinics
- Chemotherapy Centres
- Radiotherapy Centres
- Homecare
- Others
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.