Brazil Patient Adherence Programs Market Analysis
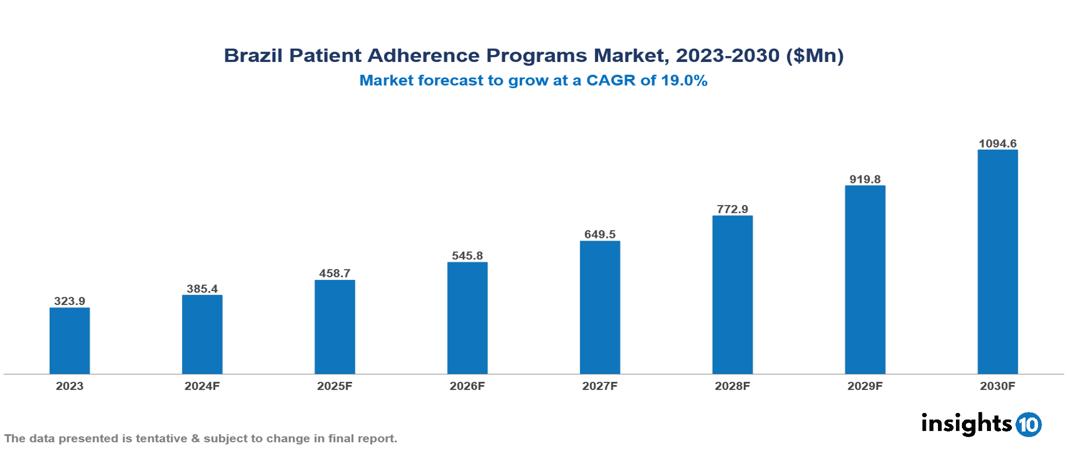
The Brazil Patient Adherence Programs Market was valued at $323.9 Mn in 2023 and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 19.0% from 2023 to 2030, to $1094.6 Mn by 2030. The key drivers of the market include increasing non-adherence, rising chronic conditions, and an aging population. The prominent players in the Brazil Patient Adherence Programs Market are Amil, Bradesco Saude, Novartis, Sanofi, and Pfizer, among others.
Buy Now

Brazil Patient Adherence Programs Market Executive Summary
The Brazil Patient Adherence Programs market is at around $323.9 Mn in 2023 and is projected to reach $1,094.6 Mn in 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 19% during the forecast period.
A patient adherence program aims to ensure that patients follow prescribed medication regimens to improve treatment outcomes, using both direct and indirect methods to assess adherence. Direct methods include monitoring therapy by measuring drug levels, metabolites, or biological markers in blood or urine, and confirming medication intake. Indirect methods, more commonly used, involve patient self-reports, pill counts, prescription refill rates, clinical response evaluations, and electronic medication monitors. Pill counts compare the number of pills taken between appointments with the prescribed dosage, while patient self-reports collect information through interviews, questionnaires, or diaries. Electronic devices such as pill bottles or blister packs track medication access to provide precise data. A widely used tool for assessing adherence is the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS), a validated and reliable questionnaire suitable for clinical use. These approaches help healthcare providers ensure consistent medication use, ultimately enhancing patient health outcomes.
The burden of several chronic illnesses is significant, rising, and concerning among the older adult population. The Brazil Patient Adherence Program Market is thus driven by significant factors such as increasing non-adherence, rising chronic disease prevalence, and an aging population. However, inadequate healthcare infrastructure, high implementation costs, and limited accessibility restrict the growth and potential of the market.
The major players in the Brazil Patient Adherence Programs Market are Amil, Bradesco Saude, Novartis, Sanofi, and Pfizer, among others.
Market Dynamics
Market Growth Drivers
Increasing Non-Adherence: In Brazil, the prevalence of non-adherence to pharmacotherapy in Brazil was 20.2%, ranging from 17.0% to 27.8% between regions. The medical field is focusing more on developing workable solutions as a result of growing recognition of the substantial negative effects of non-adherence on patient outcomes. Governments and healthcare organizations’ awareness campaigns and actions highlight the value of adherence, which increases demand and growth for patient adherence programs.
Rising Chronic Conditions: By the age of 60 years, approximately 70% of Brazilians have at least one chronic illness demonstrating the disease burden. Chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease require ongoing treatment and long-term medication adherence. The need for continuous monitoring and consistent medication use in chronic conditions necessitates adherence programs to ensure patients follow their prescribed regimens. Patient adherence programs lead to better clinical outcomes and enhanced quality of life, which creates a positive effect on the market growth.
Aging Population: Brazil is an aging country as the median age of the Brazilian population increased by 6 years since 2010 and will reach 35 years in 2022. The elderly population is more prone to risk from chronic diseases and multiple comorbidities, necessitating complex medication regimens that are difficult to manage without structured adherence programs. Adherence programs help with polypharmacy and provide monitoring and support. The aging population is thus a potential pool that can benefit from these programs which increases the market growth.
Market Restraints
Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure: By restricting access to vital healthcare services and resources required for these programs to be successful, inadequate healthcare infrastructure impedes the expansion of patient adherence initiatives. Patients face challenges in adhering to recommended therapies on a regular basis due to inadequate technology support, a lack of healthcare personnel, and poorly equipped facilities. Furthermore, inadequate infrastructure frequently results in healthcare practitioners' inability to adequately monitor and promote patient adherence, which has a negative impact on patient outcomes and diminishes confidence in these programs. As a result, these obstacles hinder market expansion by discouraging investments and limiting the efficacy and scalability of patient adherence programs.
High Implementation Costs: Establishing advanced technologies like electronic health records (EHRs), mobile health applications, telemedicine platforms, and electronic monitoring devices necessitates significant financial outlays. Additionally, the need to hire specialized personnel, such as IT experts, adherence counselors, and extra healthcare providers, adds to operational expenses. Integrating these new adherence technologies with existing healthcare systems and EHRs can be particularly complex and expensive. Thus, these all expenses related to patient adherence programs can negatively affect the market.
Limited Accessibility: Accessibility issues can hinder the expansion of the patient adherence program market, especially in regions with inadequate healthcare infrastructure. Patients in these areas often encounter obstacles like long travel distances to clinics, a scarcity of healthcare professionals, and limited access to affordable medications and adherence support. Socioeconomic challenges, such as low income and lack of insurance, further impede participation in adherence programs. These barriers reduce enrolment and engagement, thereby restricting the effectiveness and growth potential of these programs.
Regulatory Landscape and Reimbursement Scenario
The Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA), often known as the National Health Surveillance Agency, is the Brazilian regulatory body in charge of approving and monitoring a variety of products, including food, cosmetics, tobacco, medications, health services, and medical devices. ANVISA was created in 1999 and is linked to the Ministry of Health. ANVISA aims to safeguard and advance public health by conducting health surveillance over goods and services, including procedures, components, and technology that may present health concerns.
Pharmaceutical laboratories and other businesses that are a part of the pharmaceutical production cycle must register their drugs and obtain licenses from ANVISA. The agency is also in charge of creating rules that apply to clinical trials in the areas of subject safety and drug Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control (CMC). Additionally, ANVISA collaborates with the Chamber of Drug Market Regulation (CMED) and other ministry members to control pharmaceutical prices. Human clinical trials conducted ethically are overseen by an Ethics Committee (EC) affiliated with the Health Ministry. The agency inspects manufacturers, monitors drug quality, conducts post-marketing surveillance, performs pharmacovigilance activities, and controls drug marketing and promotion in collaboration with states and local governments. Furthermore, ANVISA, in collaboration with the National Industrial Property Institute (INPI), assesses patent requests pertaining to pharmaceutical items and procedures. After becoming an ICH member in November 2016, Brazil sought to facilitate regulatory approval by implementing the Common Technical Document (CTD) for the registration of medicines.
Brazil’s dual-structure healthcare reimbursement system serves both the public and private sectors. All Brazilian citizens and permanent residents are eligible for free at-the-point healthcare coverage through the Unified Health System (SUS). The government provides direct money to SUS facilities and patients do not have their own reimbursement procedure. However, due to financial limitations, SUS may have problems including lengthy wait periods and restricted access to cutting-edge therapies. A significant portion of the population is covered by private health insurance, which provides a greater choice of treatments and faster wait times than SUS. Private insurance firms pay medical providers according to prearranged contracts or schedules of fees. Methods of reimbursement may differ but usually include: Fee-for-Service (FFS) which provides payment according to the quantity of services rendered; Diagnosis Related Groups (DRGs) assign a predetermined cost for treating a certain illness; and in Managed Care Networks, the providers under contract offer discounted services.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Here are some of the major key players in the Brazil Patient Adherence Programs Market:
- Amil
- Bradesco Saude
- Novartis
- Sanofi
- Pfizer
- Memed
- PillBox Pharmacy
- Portal Telemedicina
- Droga Raia
- Pague Menos
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Service Overview
1.2 Global Scenario
1.3 Country Overview
1.4 Healthcare Scenario in Country
1.5 Healthcare Services Market in Country
1.6 Recent Developments in the Country
2. Market Size and Forecasting
2.1 Market Size (With Excel and Methodology)
2.2 Market Segmentation (Check all Segments in Segmentation Section)
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Market Drivers
3.2 Market Restraints
4. Competitive Landscape
4.1 Major Market Share
4.2 Key Company Profile (Check all Companies in the Summary Section)
4.2.1 Company
4.2.1.1 Overview
4.2.1.2 Product Applications and Services
4.2.1.3 Recent Developments
4.2.1.4 Partnerships Ecosystem
4.2.1.5 Financials (Based on Availability)
5. Reimbursement Scenario
5.1 Reimbursement Regulation
5.2 Reimbursement Process for Services
5.3 Reimbursement Process for Treatment
6. Methodology and Scope
Brazil Patient Adherence Programs Market Segmentation
By Type
- Hardware centric
- Software centric
By Medication
- Cardiovascular
- Nervous System
- Diabetes
- Gastrointestinal
- Oncology
- Rheumatology
- Others
Methodology for Database Creation
Our database offers a comprehensive list of healthcare centers, meticulously curated to provide detailed information on a wide range of specialties and services. It includes top-tier hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic facilities across 30 countries and 24 specialties, ensuring users can find the healthcare services they need.
Additionally, we provide a comprehensive list of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) based on your requirements. Our curated list captures various crucial aspects of the KOLs, offering more than just general information. Whether you're looking to boost brand awareness, drive engagement, or launch a new product, our extensive list of KOLs ensures you have the right experts by your side. Covering 30 countries and 36 specialties, our database guarantees access to the best KOLs in the healthcare industry, supporting strategic decisions and enhancing your initiatives.
How Do We Get It?
Our database is created and maintained through a combination of secondary and primary research methodologies.
1. Secondary Research
With many years of experience in the healthcare field, we have our own rich proprietary data from various past projects. This historical data serves as the foundation for our database. Our continuous process of gathering data involves:
- Analyzing historical proprietary data collected from multiple projects.
- Regularly updating our existing data sets with new findings and trends.
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy through rigorous validation processes.
With extensive experience in the field, we have developed a proprietary GenAI-based technology that is uniquely tailored to our organization. This advanced technology enables us to scan a wide array of relevant information sources across the internet. Our data-gathering process includes:
- Searching through academic conferences, published research, citations, and social media platforms
- Collecting and compiling diverse data to build a comprehensive and detailed database
- Continuously updating our database with new information to ensure its relevance and accuracy
2. Primary Research
To complement and validate our secondary data, we engage in primary research through local tie-ups and partnerships. This process involves:
- Collaborating with local healthcare providers, hospitals, and clinics to gather real-time data.
- Conducting surveys, interviews, and field studies to collect fresh data directly from the source.
- Continuously refreshing our database to ensure that the information remains current and reliable.
- Validating secondary data through cross-referencing with primary data to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Combining Secondary and Primary Research
By integrating both secondary and primary research methodologies, we ensure that our database is comprehensive, accurate, and up-to-date. The combined process involves:
- Merging historical data from secondary research with real-time data from primary research.
- Conducting thorough data validation and cleansing to remove inconsistencies and errors.
- Organizing data into a structured format that is easily accessible and usable for various applications.
- Continuously monitoring and updating the database to reflect the latest developments and trends in the healthcare field.
Through this meticulous process, we create a final database tailored to each region and domain within the healthcare industry. This approach ensures that our clients receive reliable and relevant data, empowering them to make informed decisions and drive innovation in their respective fields.
To request a free sample copy of this report, please complete the form below.
We value your inquiry and offer free customization with every report to fulfil your exact research needs.








































