Global Healthcare Regulatory, and Reimbursement Landscape
The global healthcare industry is shaped by regulations and reimbursement policies that govern how medical products and services are delivered, accessed, and paid for. These regulations vary across countries and cover areas such as drug approvals, clinical trials, and data privacy. Reimbursement models determine how healthcare providers are compensated and impact treatment decisions and costs. International organizations aim to harmonize standards and guidelines. Understanding this landscape is crucial for stakeholders, including healthcare providers, companies, insurers, policymakers, and patients.
United States of America (USA)
Regulatory Bodies
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- Founded on 30 June 1906, US FDA ensures the efficacy and safety of drugs, medical devices, and other healthcare products
- Enforcement: Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C) enforcement, but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations
- Collaboration: The USFDA works frequently with many federal agencies like the Department of Agriculture, the Drug Enforcement Administration, Customs and Border Protection, and the Consumer Product Safety Commission
FDA at a Glance
- FDA oversees the safety of >$2.1 Tn worth of food, tobacco, and medical products produced in the US and abroad
- FDA-regulated products account for about 15 cents of every dollar spent by US consumers
- There are ~671 FDA-Licensed Biologics products
- FDA oversees >6,500 medical device products
- There are ~1,600 FDA- approved animal drug products
- FDA regulates 75% of the US food supply: except meat, poultry, and some egg products
- FDA-regulated products account for 16% of US imports and 17% of exports
- FDA oversees over 1 lakh tobacco products, not including ENDS
- FDA regulations cover 35000 produce farms, 3,00,000 restaurant food establishments, and 10,500 vending machine operators
Registered Facilities
FDA – regulated products are manufactured or handled at nearly 3,00,000 registered facilities, >50% of which are outside of the US
US FDA Registered Facilities
| Program | Domestic | Foreign | Total |
| Animal drugs | 980 | 701 | 1681 |
| Animal Food | 18603 | 8281 | 26884 |
| Biologicals | 5273 | 659 | 5932 |
| Human Drugs | 4791 | 5717 | 10508 |
| Human Food | 91112 | 133569 | 224681 |
| Medical Devices | 13010 | 12891 | 25901 |
| Tobacco | 2035 | 0 | 2035 |
| Total | 135804 | 161818 | 297622 |
FDA Drug Approval Process
FDA has developed several approaches to making drugs available as quickly as possible, while still ensuring their safety and effectiveness. Here are four of these approaches:
| Fast Track | Fast track is a process designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of drugs to treat serious conditions and fill an unmet medical need |
| Breakthrough Therapy | A process designed to expedite the development and review of drugs which may demonstrate substantial improvement over available therapy |
| Accelerated Approval | These regulations allowed drugs for serious conditions that filled an unmet medical need to be approved based on a surrogate endpoint |
| Priority Review | A Priority Review designation means FDA’s goal is to take action on an application within 6 months |
Recent FDA Drug Approvals
| Drug Name | Active Ingredient | Approval Date (2023) | FDA - approved use on approval date (as of 07/17/2023) |
| Beyfortus | nirsevimab-alip | 17 July | To prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) lower respiratory tract disease |
| Ngenla | somatrogon-ghla | 27 June | To treat growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone |
| Rystiggo | rozanolixizumab-noli | 26 June | To treat generalized myasthenia gravis in adults |
| Litfulo | ritlecitinib | 23 June | To treat severely patchy hair loss |
| Columvi | glofitamab-gxbm | 15 June | To treat diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| Inpefa | sotagliflozin | 26 May | To treat heart failure |
| Posluma | flotufolastat F 18 | 25 May | To use with positron emission tomography imaging in certain patients with prostate cancer |
| Paxlovid | nirmatrelvir, ritonavir | 25 May | To treat mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in adults at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19 |
| Xacduro | sulbactam, durlobactam | 23 May | To treat hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia |
| Epkinly | epcoritamab-bysp | 19 May | To treat relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| Miebo | perfluorhexyloctane | 18 May | To treat signs and symptoms of dry eye disease |
| Veozah | fezolinetant | 12 May | To treat moderate to severe hot flashes caused by menopause |
| Elfabrio | pegunigalsidase alfa-iwxj | 9 May | To treat confirmed Fabry disease |
| Qalsody | tofersen | 25 April | To treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in adults who have a SOD1 gene mutation |
| Joenja | leniolisib | 24 March | To treat activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta syndrome |
| Rezzayo | rezafungin | 22 March | To treat candidemia and invasive candidiasis |
| Zynyz | retifanlimab-dlwr | 22 March | To treat metastatic or recurrent locally advanced Merkel cell carcinoma |
| Daybue | trofinetide | 10 March | To treat Rett syndrome |
| Zavzpret | zavegepant | 9 March | To treat migraine |
| Skyclarys | omaveloxolone | 28 Feb | To treat Friedrich’s ataxia |
| Filspari | sparsentan | 17 Feb | To reduce proteinuria in adults with primary IG-A nephropathy at risk of rapid disease progression |
| Lamzede | velmanase alfa-tycv | 16 Feb | To treat non-central nervous system manifestations of alpha-mannosidosis |
| Jesduvroq | daprodustat | 1 Feb | To treat anemia caused by chronic kidney disease for adults on dialysis for at least four months |
| Orserdu | elacestrant | 27 Jan | To treat estrogen receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, ESR1-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer |
| Jaypirca | pirtobrutinib | 27 Jan | To treat relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma in adults who have had at least two lines of systemic therapy, including a BTK inhibitor |
| Brenzavvy | bexagliflozin | 20 Jan | To improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus as an adjunct to diet and exercise |
| Leqembi | lecanemab-irmb | 6 Jan | To treat Alzheimer’s disease |
FDA Medical Device Approval Process
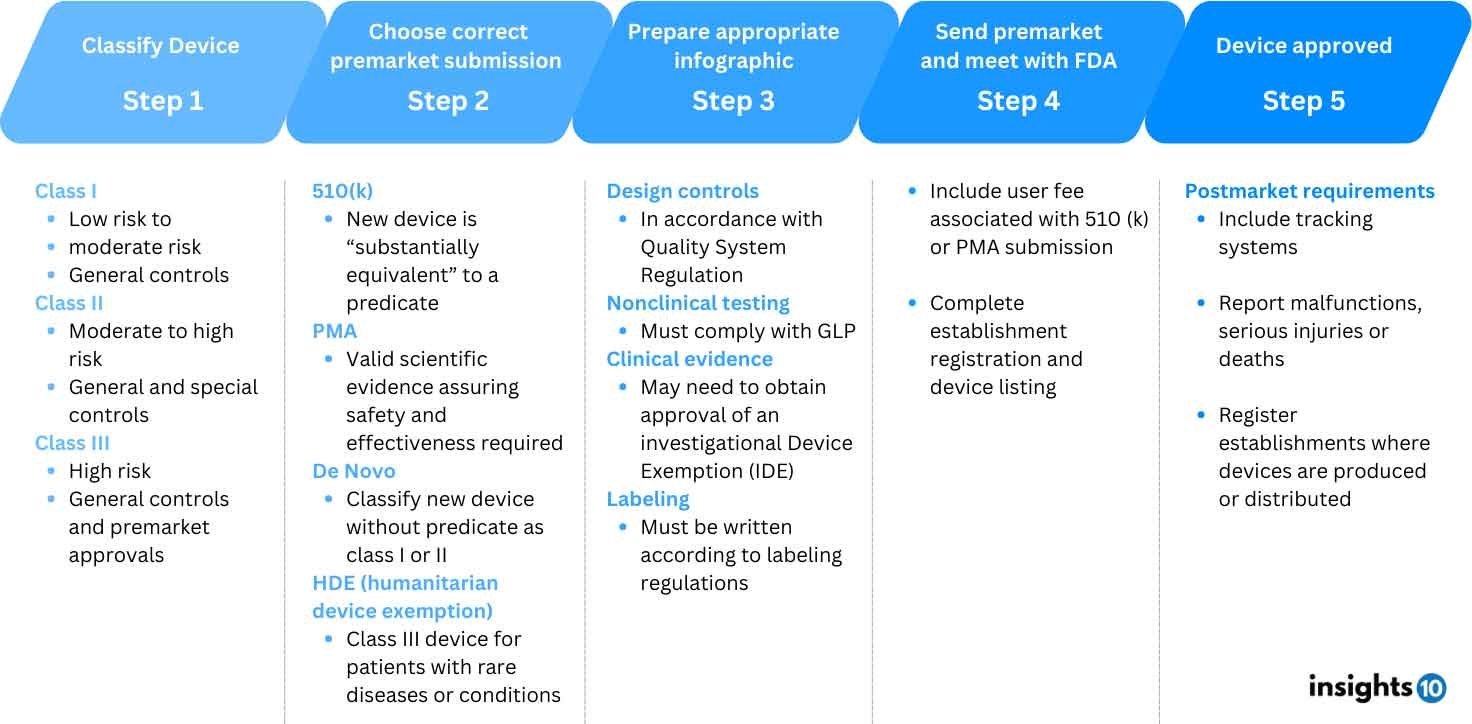
Office of Regulatory Affairs (ORA)
ORA inspects regulated products and manufacturers conducts sample analyses of those products, and reviews imported products offered for entry into the US
- Mission: The ORA's mission is to promote the responsible conduct of research and assure compliance with federal, state, and university regulations
- Responsibilities
- ORA is the lead office for all agency field activities of the FDA
- ORA also provides full-service oversight and consultation for regulatory, clinical, non-clinical, manufacturing, data management, biostatistics, and other regulated activities
- Collaboration: The ORA works with state, local, tribal, territorial, and foreign counterparts to further the FDA's mission
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
- CMS is a federal agency involved in the administration of Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
- CMS is responsible for ensuring that healthcare providers are reimbursed for services provided to eligible beneficiaries
Insurance
- In 2021, 91.7% of the population had health insurance coverage at some point during 2021
- 66% of people had private health insurance
- Employer-based insurance was the most common subtype of health insurance in the civilian, noninstitutionalized population (54.3%), followed by Medicaid (18.9%), Medicare (18.4%), direct-purchase insurance (10.2%), TRICARE (2.5%), and VA and CHAMPVA health care (1%)
Health Insurance Coverage Status in the US
| Coverage Type | 2020 | 2021 | Change % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 3,27,521 | 3,28,074 | |
| Any health plan | 2,99,230 | 3,00,887 | 0.4 |
| Any private plan | 2,17,896 | 2,16,366 | –0.6 |
| Employment-based | 1,78,737 | 1,78,285 | –0.2 |
| Direct-purchase | 33,869 | 33,555 | –0.1 |
| Marketplace coverage | 10,924 | 11,389 | 0.1 |
| TRICARE | 9,165 | 8,299 | –0.3 |
| Any public plan | 1,12,925 | 1,17,095 | 1.2 |
| Medicare | 58,541 | 60,226 | 0.5 |
| Medicaid | 58,778 | 61,940 | 0.9 |
| VA and CHAMPVA | 2,967 | 3,151 | 0.1 |
| Uninsured | 28,291 | 27,187 | –0.4 |
India
Regulatory Bodies
Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI)
- DCGI is the Central Licensing Authority in Indian regulations and is responsible for regulating drugs and medical devices in India
- Every trial site must be overseen by an Ethics Committee (EC) registered with the DCGI
- DCGI is the final regulatory authority for the approval of clinical trials in India
Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO)
CDSCO is an agency of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and is responsible for regulating medical devices in India.
Zonal Offices:
- 06 zonal offices- responsible for the clearance of food and drug products
- 04 sub-zonal offices
- 13 port offices
- 07 laboratories spread across the country
Responsibilities
- Approval of new drugs, the conduct of clinical trials
- Lay down the standards for drugs
- Control the quality of imported drugs in the country
- Coordinates activities of State Drug Control Organizations by providing expert advice with a view to bringing about uniformity in the enforcement of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is responsible for health policy in India and all government programs relating to family planning, monitoring the universal healthcare system, and approving medical facilities in India
- The Minister of Health and Family Welfare holds cabinet rank as a member of the Council of Ministers
- The current minister is Mansukh L. Mandaviya, while the current Minister of State for health are Dr. Bharati Pawar and S. P. Singh Baghel
Reimbursement Process in India
The reimbursement models for healthcare services in India are complex and vary depending on the type of healthcare service or product. Here are some of the prevailing reimbursement models for healthcare services in India:
- Tax-based funding: Tax-based funding is one of the basic healthcare payment methods available in India. The government uses tax revenue to fund healthcare services and programs
- Private health insurance: Private health insurance is available in India, but uptake is low. Health insurance is seen as a strategy to enhance access to healthcare services and products
- Donors: Donors, including international aid groups and non-governmental organizations, provide funding for healthcare services and programs in India
- Fee-for-service model: A fee-for-service model accounts for 82% of overall healthcare expenditure in India, equating to 4.2% of GDP. This model is prevalent in critical care services in India
- Out-of-pocket expenditure: Currently India does not have a mechanism for reimbursement of drugs, biologics, and medical devices
- The MoHFW oversees reimbursement-related procedures
- Health services provided by public sectors are either subsidized or free of charge
- Medicines provided by each healthcare unit from the hospital formulary, based on the National Lists of Essential Medicines (NLEM), are also provided free of charge
- The NLEM is regulated by the National Pharmaceuticals Pricing Authority (NPPA) and includes all the formulations that fall under the government’s price regulation mechanism
- In 2011, the MoHFW published the 4th Edition of NFI to address the vast expansion in the range of new drugs and their formulations
- NFI is a guidance document for medical practitioners, pharmacists, nurses, medical and pharmacy students, and other healthcare professionals and stakeholders in the healthcare system. The drugs contained in NFI are used for rational and economic prescribing
- In 2011, the NLEM was revised again and had 348 medicines. In 2015, a total of 106 medicines were added and 70 deleted; the NLEM 2015 now contains a total of 376 medicines
- As of June 2018, 851 medicines are regulated under Revised Schedule - I based on NLEM 2015, including 4 medical devices such as Cardiac stents, drug-eluting stents, condoms, and intra-uterine devices
- In July 2018, MoHFW constituted the Standing National Committee on Medicine (SNCM) to revise the NLEM every few years
- Even under the Union Budget 2023-24, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has been allocated INR 89,155 crore, a surge of 3.43% compared to INR 86,200.65 crore in 2021-22
- Approximately 514 Mn (37% population) people across India were covered under health insurance schemes in 2021
- Nearly 400 Mn Indians have zero access to health insurance
- Around 70% of the population is estimated to be covered under public health insurance or voluntarily private health insurance
- The gross written premium of the Indian health insurance industry was valued at over INR 637 Bn in 2021
Number of Individuals and Families Eligible or Covered, by Health Insurance Scheme Type
| Individuals Eligible or Covered (cr.) | Population Eligible (%) | Families Eligible or Covered (cr.) | |
| Government Subsidized Schemes | 69 | 51% | 15.3 |
| AB-PMJAY (w/o State Extension Schemes) | 49 | 36% | 10.9 |
| AB-PMJAY State Extension Schemes | 20 | 15% | 4.4 |
| Social Health Insurance Schemes | 14 | 10% | 3.6 |
| Employees’ State Insurance Scheme (ESIS) | 13.6 | 10% | 3.5 |
| Central Government Health Scheme | 0.4 | 0.30% | 1.13 |
| Private Voluntary Health Insurance (PVHI) | 11.4 | 9% | 2.6 |
| Total Eligible or Covered (assuming no overlap) | 94.5 | 70% | 21.5 |
| Total Population / Families | 135 | 30 | |
| Uncovered Population / Families | 40.5 | 30% | 8.5 |
- Premiums from India’s life insurance industry are expected to reach Rs. 24 lakh crore ($ 317.98 Bn) by FY31
- In terms of insurance density, India’s overall density stood at $78 in FY21
UAE
- UAE is home to the regional headquarters and production sites of most of the world's leading global pharmaceutical businesses
- In terms of US$, the pharmaceutical market grew from $2.9 Bn in 2017 to $3.5 Bn in 2020. The market is expected to grow further at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2021 to $5.6 Bn in 2027
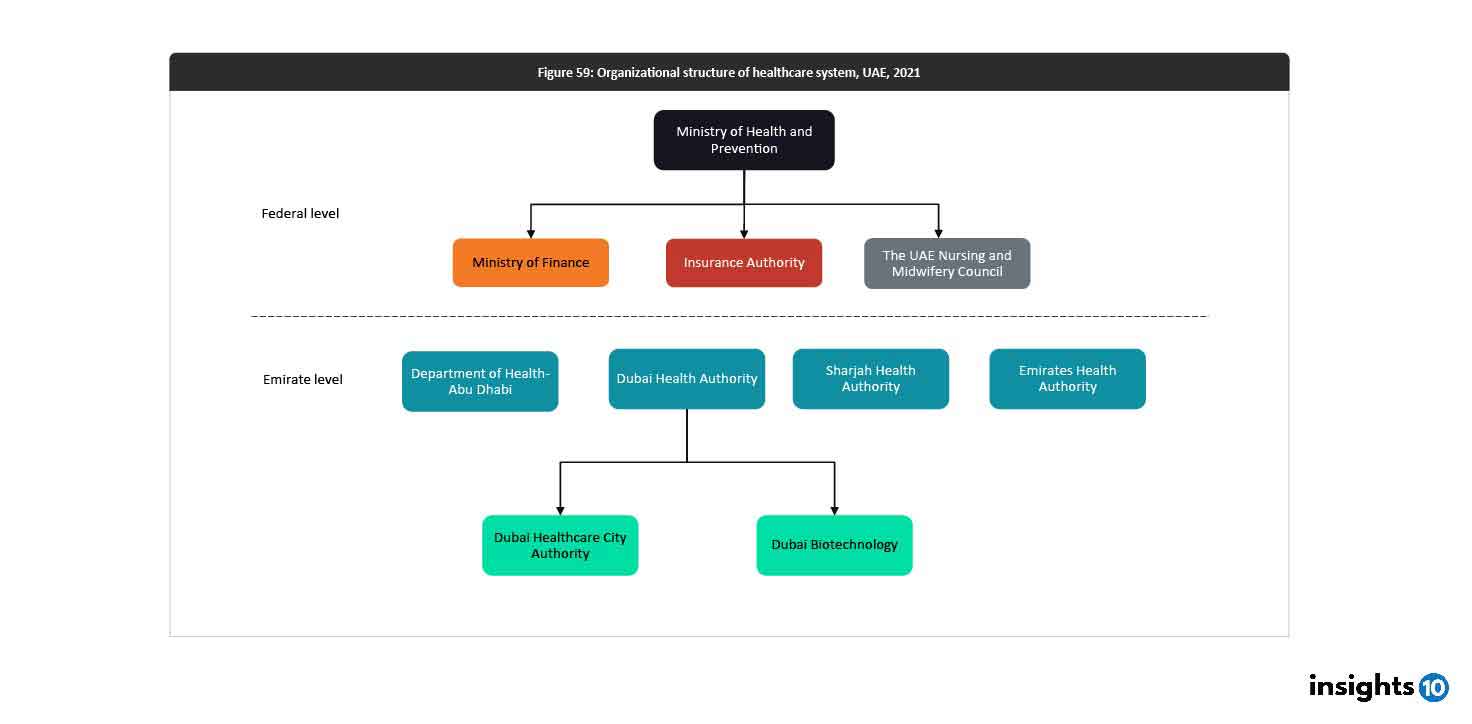
Regulatory Bodies
The UAE's healthcare system is governed by several federal and emirate-level authorities:
- MOHAP: The main federal authority responsible for an effective healthcare system
- Ministry of Finance (MOF) and Insurance Authority (IA): Federal authorities involved in the insurance aspects of healthcare
- HAAD: Aims to enhance healthcare quality and access through compulsory health insurance
- DHA: Acts as both a regulator and operator in Dubai's healthcare industry
- EHA: Similar regulatory functions as HAAD and DHA
- Sharjah Health Authority (SHA): Regulates the healthcare system in the Emirate of Sharjah
- In addition, Dubai Healthcare City (DHCC) provides a tax-free zone for healthcare-related enterprises with attractive investment prospects and incentives such as 100% foreign ownership and customs duty exemptions
Overview of Insurance Providers, UAE
The UAE has a government-funded healthcare system that offers affordable or free health services to its nationals at public facilities. The Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) provides an online platform for patients to apply for a Health Card, granting access to healthcare services at MOHAP facilities.
In Ajman, the government ensures health insurance coverage for its employees through a program called Thiqa. Thiqa provides comprehensive coverage for inpatient and outpatient treatment, with co-insurance for non-emergency services and dental, pharmaceutical, and medical equipment expenses at private network providers.
The Thiqa program is managed by the National Health Insurance Company-Daman on behalf of the Government of Abu Dhabi. Established in 2005, Daman is the leading health insurer in the UAE, serving around 3,000,000 members.
In Dubai, several health insurance programs, such as Enaya, iPROMeS, ISAHD, and SAADA, cater to different segments of the population, including government employees, residents, and visitors. In December 2021, these programs were unified under the name "Enaya" to provide integrated and high-quality medical services.
Additionally, Dubai introduced the Dubai Health Insurance Law No. 11 in 2013, requiring employers to provide basic health insurance coverage to their employees and sponsors to provide coverage to individuals under their sponsorship. The Essential Benefits Plan (EBP) is the basic health insurance plan that came into effect in stages from January 2014.
Issue of Healthcard in UAE, 2021
The MOHAP oversees health insurance coverage in other Emirates, with some Emirates having their own healthcare institutions. Sharjah, for example, extended health insurance to all citizens aged 55 years and older and plans to expand coverage to all citizens.
Private Health Insurance Providers
| Merge | Turnover | |
|---|---|---|
| AED (Mn) | USD (Mn) | |
| Orient Insurance | 5008 | 1363 |
| Oman Insurance | 3539 | 963 |
| Union Insurance | 900 | 245 |
| Takaful emarat | 584 | 159 |
| Al Dhafra Insurance | 315 | 86 |
| Alliance Insurance | 304 | 83 |
| AXA Green Crescent | 52 | 14 |
| Sharjah Insurance | 25 | 7 |
The UAE has several local and foreign private insurance providers. The total health insurance market accounted for AED19.4 Bn ($5.3 Bn), where foreign companies accounted for AED4.9 Bn ($1.3 Bn) and national companies accounted for AED14.4 Bn ($3.9 Bn). The Oman Insurance Company (OIC)/Bupa is headquartered in Dubai. OIC is the biggest insurer in the UAE and one of the leading insurance companies in the MENA region and provides group health insurance and individual health insurance plans, which are administered internationally by the British healthcare giant Bupa Global.
Reimbursement process
The UAE follows a formulary procedure for the reimbursement of medicinal products. In 2012, MOHAP published the 12th edition of the UAE drug formulary and an administrative circular on new procedures for the drug formulary application
Pharmaceutical Reimbursement Process, UAE, 2021
Europe
In Europe, there are several regulatory bodies involved in healthcare and drug approval, import, and export. These organizations play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of medicines and medical devices. Here are some of the key regulatory bodies:
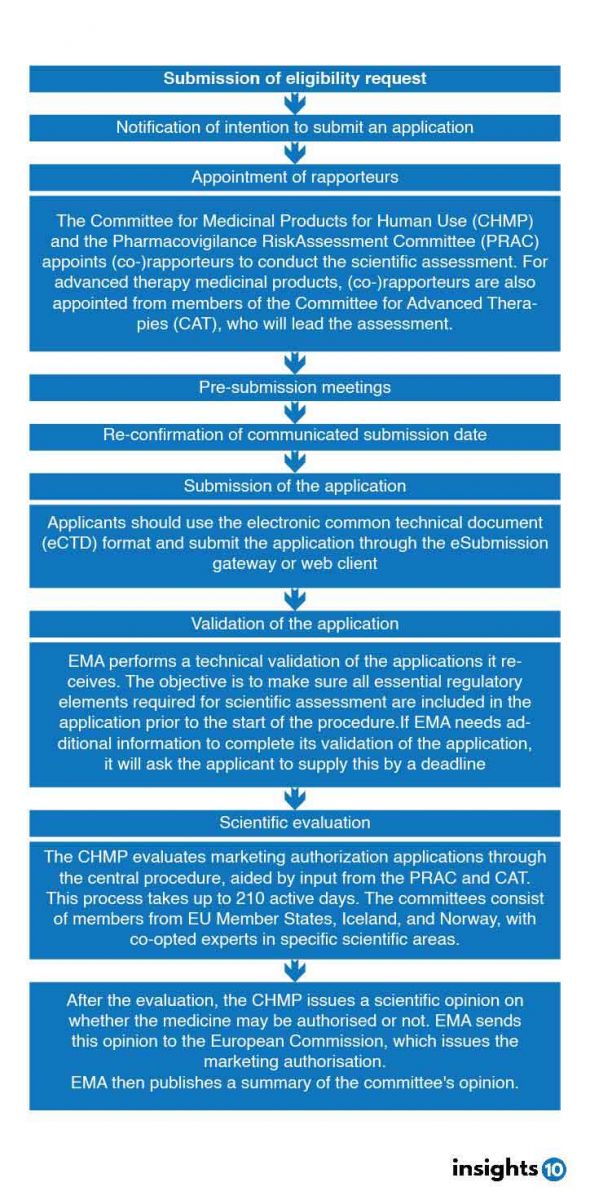
European Medicines Agency (EMA): It is responsible for the scientific evaluation, supervision, and safety monitoring of human and veterinary medicines in the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA). It authorizes and monitors medicines in the EU, and companies can apply to it for a single marketing authorization, which allows them to market the medicine throughout the EU and the EEA
Bundesinstitut für Arzneimittel und Medizinprodukte (BfArM): BfArM is the largest drug approval authority in Europe. It contributes its expertise to the scientific committees of the EMA
European Union (EU): The EU as a whole has a significant influence on access to medicines in non-EU countries. It is a key pharmaceutical exporter to low- and middle-income countries, a trade hub for treatments in transit, and a major global health donor for drug development and procurement
US Food and Drug Administration (FDA): While not based in Europe, the FDA has an office in Europe that serves as the lead for the FDA's on-site presence in Europe. It works on joint European-US projects and aims to strengthen the safety, quality, and effectiveness of medical products and food produced in Europe for export to the US
Drug Approval Process
Insurance
1. European insurance in 2020
- €2.8 Bn Claims & benefits paid per day
- €1010 Bn Total claims & benefits paid
- €1674 Claims & benefits paid per capita
- Life benefits paid declined by 9.1%
- In 2020, insurance density in Europe was €2093 and insurance penetration was 7.43%
- Health insurance penetration in Europe grew to an average of 1.01%
- An average of €1106 per person was spent on life insurance in Europe
2. Government Health Insurance Providers in Europe
- National Health Service (NHS) - United Kingdom
- Social Security Institution (INSS) - Spain
- National Health Insurance Fund (CNAM) - France
- National Health Insurance (NEAK) - Hungary
- National Health Insurance Institute (ZNZ) - Slovenia
- National Health Fund (NFZ) - Poland
- National Health Insurance House (CNAS) – Romania
3. Private Health Insurance Providers in Europe
- Allianz Care - Operates in multiple European countries
- AXA - Offers health insurance in several European markets
- Bupa - Provides private health insurance across Europe
- Cigna - Operates in various European countries
- Generali - Offers health insurance services in several European countries
- DKV Globality - Provides private health insurance in Europe
- Aetna International - Offers health insurance plans in some European countries
| Life Insurance | Health Insurance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benefits Paid | Claims Paid | ||||
| 2019 | 2020 | Change | 2019 | 2020 | Change |
| €653 Bn | €593 Bn | -9.1% | €129 Bn | €130 Bn | 1.1% |
| Premiums | |||||
| 2019 | 2020 | Change | 2019 | 2020 | Change |
| €742 Bn | €668 Bn | -9.6% | €167 Bn | €173 Bn | 3.4% |
| Density | |||||
| 2019 | 2020 | Change | 2019 | 2020 | Change |
| €1228 | €1106 | -9.9% | €278 | €238 | 3.0% |
| Penetration | |||||
| 2019 | 2020 | Change | 2019 | 2020 | Change |
| 4.17% | 3.93% | -0.24pp | 0.95% | 1.01% | 0.07% |
Regulatory Bodies Across the World
| Country Name | Pharmaceuticals |
|---|---|
| US | Food and Drug Administration |
| Canada | Health Canada |
| UK | Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency |
| Germany | Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices -Bundesinstitut für Arzneimittel und Medizinprodukte |
| France | French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety-Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé |
| Italy | Italian Medicines Agency - Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco |
| Spain | Spanish Agency of Medicines and Medical Devices - Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios |
| Russia | Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare - Roszdravnadzor |
| Netherlands | Medicines Evaluation Board - College ter Beoordeling van Geneesmiddelen |
| Sweden | Medical Products Agency - Läkemedelsverket |
| Romania | National Agency for Medicines and Medical Devices - Agenția Națională a Medicamentului și a Dispozitivelor Medicale |
| Switzerland | Swiss Agency for Therapeutic Products - Swissmedic |
| Poland | Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products - Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych, Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych |
| Austria | Austrian Federal Office for Safety in Health Care - Bundesamt für Sicherheit im Gesundheitswesen |
| Ireland | Health Products Regulatory Authority |
| Norway | Norwegian Medicines Agency - Statens legemiddelverk |
| Denmark | Danish Medicines Agency - Lægemiddelstyrelsen |
| Belgium | Federal Agency for Medicines and Health Products - Federaal Agentschap voor Geneesmiddelen en Gezondheidsproducten in Dutch, Agence Fédérale des Médicaments et des Produits de Santé in French |
| Portugal | INFARMED - Autoridade Nacional do Medicamento e Produtos de Saúde |
| Ukraine | State Service of Ukraine on Medicines and Drugs Control |
| Bulgaria | Bulgarian Drug Agency |
| Finland | Finnish Medicines Agency - Lääkealan turvallisuus- ja kehittämiskeskus |
| Venezuela | National Institute for Hygiene - Rafael Rangel |
| Senegal | Directorate of Pharmacy and Medicines - La Direction de la Pharmacie et du Médicament |
| China | National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) |
| India | Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) |
| Japan | Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) |
| Australia | Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) |
| South Korea | Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) |
| Indonesia | National Agency of Drug and Food Control (NADFC)/ Badan Pengawas Obat dan Makanan (BPOM) |
| Hong Kong | Drug Office within the Pharmaceutical Service, Department of Health |
| New Zealand | New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority (MEDSAFE) |
| Philippines | Food and Drug Administration of the Philippines (FDA Philippines) |
| Singapore | Health Sciences Authority (HSA) |
| Malaysia | National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA) |
| Thailand | Thailand Food and Drug Administration (Thai FDA) |
| Vietnam | Drug Administration of Vietnam (DAV) |
| Brazil | National Health Surveillance Agency - Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária |
| Argentina | National Administration of Drugs, Foods, and Medical Devices - Administración Nacional de Medicamentos, Alimentos y Tecnología Médica (ANMAT) |
| Mexico | Federal Commission for the Protection against Sanitary Risk - Comisión Federal para la Protección contra Riesgos Sanitarios (COFEPRIS) |
| Ecuador | National Agency for Health Regulation, Control, and Surveillance - Agencia Nacional de Regulación, Control y Vigilancia Sanitaria (ARCSA) |
| Egypt | Egyptian Drug Authority (EDA) |
| Kenya | Pharmacy and Poisons Board (PPB) |
| South Africa | South African Health Products Regulatory Authority (SAHPRA) |
| Algeria | Directorate of Pharmacy - Algerian Ministry of Health, Population and Hospital Reform |
| Nigeria | National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC) |
| Libya | Libyan National Center for Drug Control (NCDC) |
| Tanzania | Tanzania Medicines and Medical Devices Authority (TMDA) |
| Morocco | Directorate of Medicines and Pharmacy - Ministry of Health |
| UAE | Ministry of Health & Prevention (MOHAP) |
| Saudi Arabia | Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) |
| Turkey | Turkish Medicines and Medical Devices Agency - Türkiye İlaç ve Tıbbi Cihaz Kurumu (TİTCK) |
| Lebanon | Directorate General of Pharmacy - Ministry of Public Health (MOPH) |
| Kuwait | Department of Pharmacy and Drug Control - Ministry of Health |
| Qatar | Pharmacy and Drug Control Department -Ministry of Public Health (MOPH) |

